Not all internet surveys are created equal. This exploration delves into the crucial differences in survey design, methodology, and quality. From understanding the various types of online surveys to evaluating their credibility, we’ll uncover the factors that can significantly impact the reliability and accuracy of survey results. Poorly designed surveys can lead to inaccurate conclusions and flawed research, so knowing how to identify and evaluate them is vital.
We’ll examine the common pitfalls in online survey design, highlighting issues like sample size, respondent biases, and question phrasing. Understanding these factors is key to interpreting survey results effectively and avoiding misinterpretations. We’ll also look at how to improve internet survey practices and create more reliable and trustworthy surveys.
Understanding the Variations in Internet Surveys
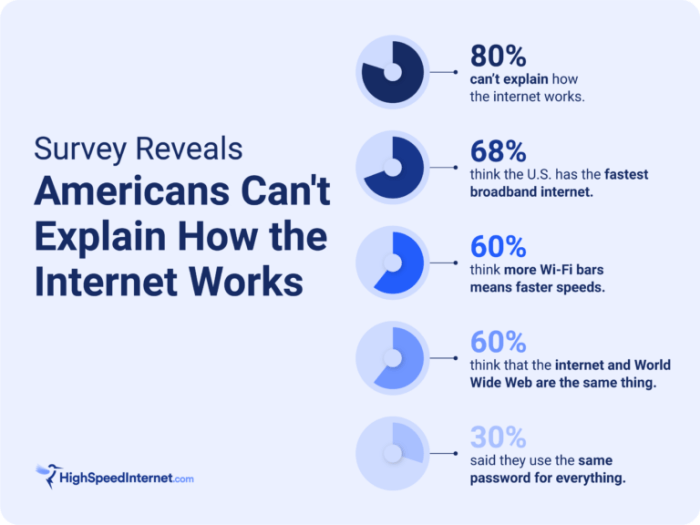
Online surveys have become ubiquitous, a crucial tool for gathering data and insights across various fields. However, the quality of information gleaned depends heavily on the survey’s design and methodology. Different approaches yield different results, and understanding these nuances is vital for interpreting survey findings accurately. A well-structured survey can provide valuable insights, while a poorly designed one can lead to misleading or inaccurate conclusions.
Different Types of Internet Surveys
Internet surveys encompass a wide spectrum of formats. These range from simple questionnaires delivered via email to more complex surveys utilizing interactive platforms. Each type has unique characteristics and strengths, influencing the kinds of data that can be collected. Simple email-based questionnaires, while easy to deploy, often suffer from low response rates. Interactive platforms, on the other hand, offer features like real-time data collection and complex branching logic, enabling more nuanced data collection.
Survey Design Methodologies
Various methodologies underpin the design of online surveys. Some commonly used methods include random sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. Each method has implications for the representativeness of the sample. Random sampling, for instance, aims to ensure every member of the target population has an equal chance of being selected, leading to a more generalizable sample. Conversely, stratified sampling involves dividing the population into subgroups (strata) before sampling, improving the representation of specific subgroups.
These methods influence the validity and reliability of the survey findings.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Different Survey Designs
Different survey designs possess varying strengths and weaknesses. For example, a survey relying on multiple-choice questions can quickly gather large amounts of data but might miss nuanced perspectives. Open-ended questions, on the other hand, allow for more in-depth responses but can be more time-consuming to analyze. The choice of design depends on the specific research objectives and the nature of the information sought.
The ability to analyze qualitative data from open-ended questions provides richer insights, while the speed of data collection from multiple-choice questions makes them ideal for broad-scale surveys.
Sample Size and Representation in Online Surveys
Sample size and representativeness are critical aspects of online surveys. A sample that accurately reflects the target population is essential for drawing valid conclusions. Insufficient sample size can lead to inaccurate generalizations about the entire population. Likewise, a sample that isn’t representative of the population can lead to biased results. The ideal sample size depends on factors like the size of the population, the desired level of precision, and the variability within the population.
Using readily available online survey tools often allows for quick data collection, but it’s crucial to ensure the sample size and methodology align with the research objectives.
Examples of Poorly Designed Internet Surveys
One example of a poorly designed survey is one that lacks clear instructions or uses ambiguous language. Another common pitfall is the use of leading questions, which can subtly influence respondents’ answers. A poorly constructed survey can result in data that is difficult to interpret or that may misrepresent the opinions of the target population. This can occur when the survey does not account for the cultural or linguistic nuances of the target audience.
Common Pitfalls in Online Survey Design
| Pitfall | Description | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ambiguous Questions | Questions with multiple interpretations. | Misleading or inaccurate data. | Clearly define the intended meaning. |
| Leading Questions | Questions that suggest a particular answer. | Biased responses. | Use neutral phrasing. |
| Insufficient Sample Size | Sample size too small to accurately represent the population. | Inaccurate conclusions. | Calculate appropriate sample size. |
| Lack of Clear Instructions | Instructions that are unclear or incomplete. | Respondents misunderstand the questions. | Provide comprehensive instructions. |
| Poor Question Wording | Questions that are poorly phrased. | Responses are difficult to interpret. | Ensure questions are clear, concise, and focused. |
| Lack of Response Options | Insufficient or inappropriate response options. | Limited insights. | Include appropriate and comprehensive response options. |
Factors Influencing Survey Quality: Not All Internet Surveys Are Created Equal
Understanding the nuances of internet surveys is crucial for extracting reliable and meaningful insights. Beyond the methodological choices in survey design and distribution, several key factors directly impact the quality and reliability of the data collected. These factors range from the survey’s length and complexity to respondent motivations and the wording of questions themselves. Careful consideration of these elements is essential for producing accurate and insightful results.Survey quality is not solely determined by the tool used; it’s a multifaceted interplay of design, participant engagement, and respondent characteristics.
The effectiveness of an online survey depends on several interacting elements, each playing a vital role in determining the accuracy and validity of the collected data. Careful attention to these influencing factors is paramount to obtaining reliable and insightful results.
Survey Length and Complexity
Survey length and complexity are directly related to participant engagement and completion rates. Long and overly complex surveys tend to decrease participant motivation and increase the likelihood of incomplete responses or careless answers. Participants often prioritize their time and effort, leading to higher dropout rates in lengthy surveys. The design of the survey, including clear instructions and logical question sequencing, can mitigate this issue.
Consider breaking down complex topics into smaller, more manageable segments. Using clear, concise language and avoiding jargon is also crucial for maintaining participant engagement.
Respondent Biases and Motivations
Respondent biases and motivations can significantly skew survey outcomes. Participants may respond in ways that align with their personal values, beliefs, or desired image. This can result in inaccurate or misleading data. Understanding potential biases is essential for interpreting results and mitigating their impact. Careful consideration of the target population’s demographics and characteristics can help identify potential biases and ensure the survey sample is representative.
Incentives can also influence responses, so it’s important to be transparent about how incentives might affect participation.
Question Wording and Phrasing
The wording and phrasing of survey questions can significantly influence participant interpretations and responses. Ambiguous or leading questions can introduce bias and yield inaccurate data. Clear, concise, and neutral language is essential. The use of specific and measurable terms, avoiding jargon or overly technical language, is critical for obtaining reliable responses. Consider pre-testing the survey with a small sample group to identify potential ambiguities or misunderstandings.
Survey Incentives and Compensation
Survey incentives and compensation play a crucial role in influencing participation rates. Participants are more likely to complete a survey if they are offered an incentive. The type and value of the incentive can vary based on the survey’s length, complexity, and the target population. However, excessive incentives can introduce a bias, skewing the sample towards participants driven primarily by the incentive.
Transparency about the use of incentives and their potential influence is crucial for ensuring the integrity of the data.
Relationship Between Survey Characteristics and Response Rates
| Survey Characteristic | Description | Impact on Response Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Survey Length | The total time required to complete the survey. | Shorter surveys generally yield higher response rates. |
| Survey Complexity | The level of difficulty and intricacy of the questions. | Simpler surveys encourage higher completion rates. |
| Question Wording | Clarity and neutrality of the questions. | Clear and unbiased questions improve accuracy and response rates. |
| Respondent Compensation | Incentives offered for participation. | Appropriate compensation can motivate participation. |
| Survey Format | Ease of navigation and user-friendliness. | Intuitive survey design increases response rates. |
Evaluating the Credibility of Internet Surveys
Scrutinizing online surveys is crucial for gleaning reliable insights. Just because a survey is conducted online doesn’t automatically equate to validity or accuracy. Various factors, from the survey’s design to the respondent pool, can significantly impact the reliability of the results. Understanding these elements is vital for anyone interpreting survey data.A critical eye and a nuanced understanding of survey methodologies are essential when evaluating online surveys.
It’s easy to get caught up in the endless stream of internet surveys, but not all are trustworthy. For example, a company like the world’s largest clothing company, worlds largest clothing co to sell online to retailers , might use surveys to gather valuable data about consumer preferences, but other surveys might just be trying to trick you into sharing personal information.
So, always be a savvy consumer and look for legitimate sources before filling out any survey.
Transparency in survey design and execution, a representative sample, and a conscious awareness of potential biases are critical components in judging the credibility of online surveys. This section delves into the key elements necessary for evaluating the credibility of internet surveys, equipping you with the tools to differentiate between sound research and potentially misleading data.
Transparency in Survey Methodology
Understanding how a survey is constructed is paramount to evaluating its credibility. Clear and detailed descriptions of the survey methodology, including the sampling strategy, question wording, and data analysis techniques, build trust and allow for critical assessment. Transparency allows readers to understand the steps taken to collect and interpret the data, fostering confidence in the results. A lack of transparency raises red flags, potentially signaling a biased or manipulated outcome.
Assessing Sample Size and Representativeness
The sample size and its representativeness are crucial indicators of survey credibility. A survey’s sample should mirror the characteristics of the target population. A large, representative sample provides greater confidence in the results’ generalizability to the broader population. Conversely, a small or unrepresentative sample limits the survey’s applicability and can introduce significant biases. For instance, a survey targeting U.S.
adults but only sampling residents of California would not be representative and its findings would not be generalizable to the entire U.S. adult population.
Identifying Potential Biases in Online Survey Design, Not all internet surveys are created equal
Online surveys are susceptible to several biases. One common pitfall is self-selection bias, where respondents are not randomly selected, but rather choose to participate. This can skew the results, as those who choose to respond may differ significantly from those who do not. Other potential biases include question wording, order effects, and response rates. Understanding and mitigating these biases is essential to ensuring the reliability and validity of the survey findings.
Examples of Surveys with Questionable Methodologies
Numerous examples exist of online surveys with questionable methodologies. Surveys with extremely small sample sizes, a lack of clarity on sampling methods, or leading questions often yield unreliable results. Surveys focusing on specific demographics or geographic regions without proper representation of the overall population raise red flags. An example would be a survey about public opinion on a new law, which only polled residents of one city or town.
Such examples underscore the need for meticulous attention to survey design and execution.
Checking for Leading Questions
Leading questions can subtly influence respondents’ answers, leading to biased results. Questions that suggest a desired answer or frame a topic in a specific way can bias responses. Critically evaluating the wording of survey questions is crucial to identifying potential biases. Avoidance of leading questions and neutral phrasing ensures objective results. For example, a question like “Don’t you think our local government is doing a terrible job?” is leading, as it implies a negative assessment.
Determining the Reliability of Survey Data
Methods for determining the reliability of survey data include examining response rates, looking for consistency in responses, and comparing results to other reputable sources. A low response rate can indicate potential biases. Inconsistencies in responses might signal problems with the survey instrument or the respondents. Comparing the survey results to other credible research can help corroborate findings and identify potential inaccuracies.
Criteria for Evaluating Survey Credibility
| Evaluation Criteria | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | Clear explanation of methodology, including sampling, question wording, and analysis. | Detailed description of the survey’s sampling frame and the process used to select respondents. |
| Sample Size and Representativeness | Adequate sample size and accurate representation of the target population. | A survey targeting U.S. adults with a sample that accurately reflects the demographic makeup of the U.S. population. |
| Bias Identification | Awareness and mitigation of potential biases in the survey design, such as self-selection bias, question wording, and order effects. | Use of randomized sampling techniques to reduce self-selection bias and neutral wording in questions. |
| Methodology Validity | Sound research design, reliable methods, and appropriate analysis techniques. | Use of established statistical methods to analyze survey data and proper controls for confounding variables. |
| Leading Questions | Absence of leading or suggestive question wording. | Questions that avoid emotional language or presumptions and are framed neutrally. |
| Data Reliability | High response rate, consistent responses, and corroboration with other sources. | A high response rate and comparison of the results to previously published studies on the topic. |
Implications of Unequal Survey Quality
The internet has democratized access to surveys, allowing for a wider range of voices and perspectives. However, this accessibility also introduces a significant risk: the quality of internet surveys can vary dramatically. Poorly designed surveys can yield inaccurate results, leading to flawed conclusions and potentially harmful consequences in various fields. Understanding the implications of these variations is crucial for informed decision-making and the advancement of sound research.Surveys are integral to gathering data for a multitude of purposes, from market research to academic studies and policy formulation.
When these surveys are flawed, the results can distort the understanding of the target population, leading to misguided decisions with real-world consequences. This is particularly concerning in fields like healthcare, where incorrect data can directly affect patient care, or in political campaigns, where inaccurate polling data can lead to misguided policy strategies.
Examples of Inaccurate Conclusions from Poor Survey Design
Poorly worded questions, leading questions, and a lack of clarity in the survey’s instructions can skew results. For example, a survey about environmental awareness might use emotionally charged language, leading respondents to answer in a way that reflects their feelings rather than their actual beliefs. Likewise, a survey about a new product might present the product in an overly positive light, potentially inflating its perceived desirability.
It’s easy to get caught up in the allure of quick internet surveys, but not all are built the same. Companies like the ones behind CBS’s recent majority stake in a web portal are constantly looking for ways to gather data, which can influence their business decisions. Ultimately, the value and reliability of any online survey still depends on its methodology and the motivations of the organization behind it.
So, be a savvy survey-taker and always question the source.
Furthermore, a survey with a small or unrepresentative sample size can lead to inaccurate conclusions about the larger population.
Potential Consequences of Flawed Survey Results on Decision-Making
Flawed survey results can lead to misguided decisions in various fields. In market research, inaccurate data might result in a company launching a product that does not resonate with consumers, leading to significant financial losses. In academic research, inaccurate data might lead to incorrect conclusions about the effectiveness of a new treatment, potentially delaying the development of effective interventions.
In political campaigns, flawed survey data can result in the allocation of resources to ineffective strategies. In healthcare, incorrect data can lead to the development and implementation of ineffective treatments, leading to harm to patients.
Impact of Inaccurate Data on Research Outcomes
Inaccurate data significantly impacts research outcomes. If a research study uses a survey with flawed methodology, the findings are unreliable and potentially misleading. The results may be incorrectly interpreted, leading to the misdirection of future research efforts. For instance, a survey about the effectiveness of a new teaching method, conducted with a biased sample, might suggest a positive impact when in reality the method is ineffective.
It’s easy to get caught up in the allure of quick internet surveys, but not all are built the same. Sometimes, they’re just trying to gather data for marketing purposes, not necessarily seeking genuine feedback. Fortunately, there are network solutions to give ups link to small business network solutions to give ups link to small business that can help bridge that gap.
Ultimately, understanding the source and purpose of the survey is key to recognizing the true value (or lack thereof) of any online poll.
Such inaccurate data can hinder progress in various fields by leading to incorrect assumptions and faulty conclusions.
Negative Consequences of Poor Internet Surveys
| Issue | Description | Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Biased Sampling | Surveys that do not represent the target population accurately, leading to skewed results. | Misleading conclusions, incorrect predictions, ineffective policies, and wasted resources. |
| Poorly worded questions | Ambiguous, leading, or confusing questions that do not accurately capture respondent’s opinions. | Inaccurate data, unreliable results, and flawed decisions. |
| Low response rate | A low percentage of the targeted population responding to the survey. | Limited generalizability of results, misrepresentation of the target population, and potentially inaccurate conclusions. |
| Inadequate sample size | Surveys conducted with a sample size too small to represent the target population accurately. | Unreliable results, inability to draw meaningful conclusions about the target population, and incorrect inferences. |
| Lack of anonymity | Surveys that do not ensure respondent anonymity. | Reduced willingness to provide honest and accurate responses, potentially affecting the accuracy of the data collected. |
Improving Internet Survey Practices
Online surveys have become ubiquitous, offering a convenient and cost-effective way to gather data. However, the quality of internet surveys varies significantly. This difference stems from factors like survey design, respondent engagement strategies, and the overall credibility of the survey platform. Improving internet survey practices is crucial for ensuring reliable and trustworthy data collection.
Strategies for Developing High-Quality Online Surveys
High-quality online surveys require careful planning and execution. A clear understanding of the research objectives is paramount. Defining the target population, selecting appropriate survey questions, and pilot testing the survey are essential steps in this process. This iterative approach ensures the survey accurately measures the desired information and effectively reaches the intended audience.
Framework for Creating Reliable and Trustworthy Internet Surveys
A robust framework for internet surveys should incorporate several key elements. Firstly, the survey should be designed with clarity and conciseness. Avoid ambiguity in questions and use appropriate response scales. Secondly, respondent anonymity and confidentiality must be explicitly addressed. Finally, ensuring the survey’s security and integrity through encryption and validation procedures are crucial.
Implementing these measures strengthens the survey’s credibility and fosters respondent trust.
Tips for Improving the Design of Internet Surveys
The design of online surveys significantly impacts the quality of data collected. Using clear and concise language is essential for comprehension. Employing visually appealing and user-friendly layouts enhances respondent engagement. The survey should be organized logically, guiding respondents through the questions in a structured manner. Carefully structuring the survey to reduce respondent burden is critical.
Techniques for Ensuring Survey Respondent Engagement
Respondent engagement is critical for obtaining high-quality data. Using engaging question formats, such as visual aids or interactive elements, can increase participation. Offering incentives, such as small rewards or recognition, can also motivate respondents. Personalization of the survey experience, tailoring the questions based on previous answers, can maintain respondent interest. Communicating clearly the importance of the survey and its impact to the audience will foster engagement.
Examples of Best Practices in Online Survey Design
Several examples illustrate best practices in online survey design. Surveys using pre-tested questions and a logical flow are effective. Surveys incorporating clear instructions and visually appealing layouts also demonstrate good practices. Utilizing a variety of question types, such as multiple choice, rating scales, and open-ended questions, provides comprehensive data. A survey should have a clear and concise introduction that explains the purpose of the study and how their responses will be used.
Guide for Survey Creators to Ensure Accuracy and Reliability
Creating a guide for survey creators is vital to maintain accuracy and reliability. This guide should include detailed instructions on survey design principles, such as question wording, response scales, and logical flow. It should also cover best practices for survey administration, including respondent recruitment and data collection procedures. The guide should emphasize the importance of rigorous quality control measures throughout the survey process.
Finally, the guide should include details on data analysis and interpretation to help creators understand and use the results effectively.
Final Review
In conclusion, the quality of internet surveys varies significantly. This article emphasized the importance of critical evaluation when dealing with online surveys. By understanding the potential pitfalls, evaluating the methodology, and assessing the credibility of the survey, we can make informed decisions based on reliable data. High-quality online surveys are crucial for accurate research and informed decision-making, and we’ve explored the steps to achieve them.
The journey to better online surveys starts with understanding the nuances of their design.

