New group sends message on internet regulation, sparking a crucial debate about the future of online governance. This new initiative proposes significant changes to internet content, safety, and user privacy, promising to reshape the digital landscape. The group’s stated goals, the proposed regulations, and the potential impacts on various stakeholders are at the heart of this discussion, generating considerable public reaction and debate.
The group’s proposals touch upon a wide range of issues, from online safety measures and user privacy concerns to the potential economic and societal effects of their regulations. They aim to address the complexities of internet governance in a global context, potentially leading to international cooperation or conflict.
Background of the New Group
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, prompting ongoing debates about internet regulation. This evolution necessitates careful consideration of the balance between innovation, user rights, and societal well-being. A newly formed group dedicated to shaping the future of internet regulation is emerging, and understanding its background provides valuable context.This group represents a critical response to the evolving challenges and opportunities presented by the internet.
Their formation reflects a growing recognition of the need for proactive measures to address the complexities of online interactions. Their perspective offers a unique lens through which to analyze the current state of internet governance.
Historical Overview of Internet Regulation Efforts
Early internet regulation efforts focused primarily on technical standards and infrastructure development. Over time, concerns about content moderation, online safety, and digital rights emerged, leading to more comprehensive regulatory frameworks. Examples include the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) in the United States, aiming to protect children’s data online, and the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), designed to strengthen data privacy rights.
These initial efforts laid the groundwork for more sophisticated and nuanced approaches to internet governance.
Composition and Motivations of the New Group
The new group comprises a diverse range of stakeholders, including academics, technologists, policymakers, and civil society representatives. Their motivations stem from a shared belief in the transformative power of the internet and the importance of shaping its trajectory responsibly. Recognizing the potential for both harm and good, they aim to establish a more balanced regulatory framework that fosters innovation while mitigating risks.
Different individuals and organizations have varied motivations; for instance, some academics might be motivated by the need for theoretical research, while others might focus on practical implications for society.
Stated Goals Regarding Internet Regulation
The group’s stated goals revolve around promoting a more inclusive, secure, and innovative internet. They aim to create a regulatory environment that:
- Facilitates the growth of emerging technologies while protecting user rights. This involves striking a delicate balance between supporting innovation and safeguarding against potential harms.
- Ensures equitable access to the internet for all individuals and communities. The group emphasizes the importance of bridging the digital divide and promoting universal connectivity.
- Combats harmful content and activities online, including hate speech, cyberbullying, and online fraud. This necessitates the development of effective tools and strategies for combating these harmful activities.
Key Individuals or Organizations Involved
The group includes prominent figures from various fields, including renowned academics in the field of digital rights and prominent technology companies with a vested interest in responsible online conduct. A comprehensive list of key participants would include:
| Name/Organization | Affiliation | Specific Role/Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Dr. Jane Doe | Professor of Digital Ethics | Expert in digital rights, leading researcher in online safety |
| Acme Corporation | Tech Company | Advocating for responsible innovation and user protection |
| The Digital Rights Foundation | Civil Society Organization | Promoting digital rights and advocating for equitable access |
This table provides a glimpse into the diverse range of individuals and organizations contributing to the group’s efforts. Their combined expertise and experience promise a significant impact on the development of future internet regulation.
Group’s Proposed Regulations
Our group proposes a comprehensive framework for internet regulation, aiming to balance freedom of expression with online safety and security. This framework acknowledges the transformative power of the internet while recognizing the need for responsible use and protection from harmful content. We believe that these regulations are crucial for fostering a more equitable and secure digital environment for all users.Our proposed regulations are designed to create a safer and more trustworthy internet ecosystem.
They address critical issues like online harassment, hate speech, and the spread of misinformation, while respecting user privacy and promoting innovation.
Proposed Measures for Online Safety and Security
The proposed regulations incorporate several measures to enhance online safety and security. These measures are categorized to ensure clarity and effectiveness. Crucially, they are designed to prevent malicious actors from exploiting online platforms.
A new group’s message on internet regulation is interesting, but it’s also worth considering how that might tie into the current economic climate. Intel, for example, recently stated that the trillion-dollar commerce forecast is too low, intel says trillion dollare commerce forecast too low , highlighting the potential for significant growth in the digital economy. This new group’s perspective on regulation could be pivotal in shaping the future of that growth.
- Content Moderation Policies: Robust content moderation policies are essential to combat harmful content, including hate speech, incitement to violence, and harassment. These policies should be transparent and clearly defined, with established appeals processes. Examples of existing successful policies include those used by social media platforms, which have evolved to include more nuanced responses to the increasing complexity of online interactions.
- Cybersecurity Measures: Platforms should be required to implement and maintain robust cybersecurity measures to protect user data and prevent cyberattacks. This includes implementing encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits. A strong example is the adoption of strong password protocols and security updates for software applications, which reduces vulnerabilities to hackers and malicious actors.
- Reporting and Enforcement Mechanisms: Clear reporting mechanisms for users to report harmful content are vital. Effective enforcement mechanisms, including penalties for violations, are essential to ensure accountability. This is similar to existing copyright infringement policies, which require clear mechanisms for reporting and handling violations.
Group’s Approach to User Privacy
User privacy is a paramount concern. The proposed regulations emphasize data minimization, user consent, and transparency in data handling practices.
- Data Minimization: Data collection should be limited to what is strictly necessary for the provision of services. This prevents unnecessary collection and storage of personal information. A good example of this is the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which mandates that companies collect and use only the data necessary for specific purposes.
- User Consent: Explicit user consent should be required for data collection and usage, with clear and accessible explanations of how data will be utilized. This principle is a cornerstone of many existing data privacy laws and reflects the importance of user autonomy in the digital sphere.
- Data Security Measures: Strong data security measures should be implemented to protect user data from unauthorized access and breaches. Encryption, secure storage, and regular security audits are essential to safeguard user privacy. Many companies use advanced encryption techniques to protect sensitive data, such as financial information.
Comparison with Existing Regulations
The proposed regulations build upon existing internet regulations, while addressing gaps and evolving challenges.
A new group is weighing in on internet regulation, a topic gaining traction with the recent push for stricter guidelines. This comes at a time when companies like SAP are taking a more assertive stance on internet practices, as seen in their aggressive approach detailed in sap goes after internet big time. Ultimately, the new group’s message on internet regulation is likely to spark further discussion and potential changes in the digital landscape.
- Existing Frameworks: The proposed regulations draw inspiration from existing frameworks such as the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) in the U.S. and the GDPR in Europe, adapting them to the current online landscape.
- Addressing Gaps: The proposed regulations address gaps in existing regulations, particularly in areas like the spread of deepfakes and online harassment. Existing laws may not adequately address the new types of harms and risks emerging in the digital world.
- Global Harmonization: A key aspect is the effort towards global harmonization of internet regulations to ensure consistency and reduce regulatory arbitrage. This approach aims to establish a more unified and predictable global internet regulatory framework.
Potential Impacts on Stakeholders
The proposed regulations will have various impacts on different stakeholders.
| Stakeholder | Potential Impacts |
|---|---|
| Users | Increased online safety and security, enhanced privacy protection, and greater trust in online services. |
| Businesses | Increased compliance costs, potential changes in business models, and adaptations to new regulatory requirements. Examples include the need for more robust cybersecurity systems and updated privacy policies. |
| Governments | Enhanced ability to regulate online activities, increased cooperation between jurisdictions, and potential for revenue generation. |
Potential Impacts and Implications
The proposed internet regulations, while intending to foster a safer and more controlled online environment, carry significant potential impacts across economic, societal, and global spheres. Understanding these potential effects is crucial for evaluating the proposed rules and ensuring a balanced approach. A thorough examination of the implications on freedom of expression, global governance, and the practical challenges of implementation is essential for informed discussion.The proposed regulations, aiming to address online harms and enhance digital security, will undoubtedly trigger a cascade of reactions, impacting everything from individual behavior to international relations.
Careful consideration of these potential impacts is paramount to shaping regulations that are both effective and equitable.
Economic Effects
The proposed regulations will have a complex and multifaceted impact on the internet economy. Positive impacts could include a reduction in cybercrime and online fraud, leading to greater consumer confidence and investment. This, in turn, could stimulate economic growth. Conversely, regulatory burdens could increase compliance costs for businesses, particularly smaller companies, potentially stifling innovation and hindering economic expansion.
- Increased compliance costs for businesses could lead to reduced investment in online services and potentially job losses. For instance, the implementation of stricter data protection regulations in the European Union has led to significant costs for businesses adapting to new compliance requirements.
- Regulations could incentivize the development of more secure and robust online infrastructure. Companies may invest more heavily in security measures to meet the demands of the new regulations, leading to the creation of new job opportunities in the cybersecurity sector.
- Restrictions on certain content could negatively impact industries reliant on online content sharing, such as the music or film industries. This could also limit the reach of independent artists and content creators.
Societal Effects
The regulations’ societal impact will be substantial, influencing how people interact, access information, and exercise their rights online. It is important to consider how these rules might affect different demographics, social groups, and regions.
- The potential for increased censorship and restrictions on freedom of expression is a critical concern. If the proposed rules are not carefully crafted, they could disproportionately affect marginalized communities or those expressing dissenting opinions. Examples of previous instances where regulations were used to silence dissent can provide valuable context.
- The regulations could foster a more transparent and accountable online environment. This could increase public trust and confidence in the internet. Increased transparency can also lead to a reduction in the spread of misinformation and harmful content.
- Potential impacts on privacy and surveillance must be thoroughly assessed. Balancing the need for security with the protection of individual privacy is a key challenge. The implications of increased surveillance for civil liberties and personal freedom need careful consideration.
Implications for Global Internet Governance
The regulations will likely influence the broader landscape of global internet governance. International cooperation and standardization will be crucial for effective implementation.
- Harmonization of regulations across different jurisdictions is essential for preventing fragmentation and ensuring the smooth functioning of the internet. A lack of global consensus could lead to a patchwork of regulations that are difficult to navigate.
- The regulations could create new opportunities for international cooperation in addressing cross-border online harms. This could involve the sharing of best practices and the development of joint strategies.
- Differences in regulatory approaches across countries could lead to a digital divide, where some regions have greater access to services and information than others.
Impact on Freedom of Expression Online
The proposed rules’ impact on freedom of expression is a critical consideration. Balancing the need for security and safety with the right to free speech online is a complex task.
- The regulations could lead to restrictions on freedom of expression online if not carefully designed. It’s important to consider the potential for abuse of power by authorities and the potential for unintended consequences.
- Regulations can help create a more tolerant and inclusive online environment by addressing hate speech and harmful content. This could protect vulnerable groups and individuals from online harassment and discrimination.
- The potential for the regulations to be used to suppress dissent or silence marginalized voices must be addressed through robust oversight mechanisms.
Challenges and Solutions to Implementation
Implementing the proposed regulations will face several challenges. Careful consideration of these challenges and the development of appropriate solutions is essential for success.
- Ensuring effective enforcement of the regulations will be challenging. A lack of resources or capacity could lead to inconsistent application of the rules.
- Developing effective and reliable mechanisms for dispute resolution will be essential for ensuring fairness and transparency. Clear procedures for appealing decisions are necessary.
- Collaboration between governments, internet service providers, and technology companies will be crucial for successful implementation. A coordinated approach will ensure that the regulations are effectively applied and that stakeholders are supported.
Public Reaction and Debate

The internet, a global network of interconnected computers, has become an indispensable part of modern life. This necessitates careful consideration of regulations to ensure responsible use and address potential harms. The newly proposed regulations, aiming to foster a safer and more equitable digital environment, have ignited a vibrant public discourse, prompting diverse reactions from various sectors.Public responses to the proposed regulations are varied and complex, reflecting the multifaceted nature of the internet’s impact on society.
Different stakeholders hold differing perspectives, leading to a nuanced and often contentious debate. Understanding these viewpoints is crucial to evaluating the potential consequences of the proposed regulations and ensuring their efficacy.
Public Responses to the Proposed Regulations
The proposed regulations have elicited a broad spectrum of responses, ranging from enthusiastic support to staunch opposition. Public forums, social media platforms, and online news outlets have become battlegrounds for passionate arguments for and against the new rules. This range of opinions highlights the significant impact the internet has on individuals and communities.
A new group is weighing in on internet regulation, which is a timely topic given the current pressures in the financial sector. For instance, the recent news surrounding net bnk under merger pressure ( net bnk under merger pressure ) highlights the interconnectedness of online services and traditional finance. Ultimately, this new group’s message on internet regulation will likely spark further discussion and debate, especially considering the broader implications for online activity.
Different Viewpoints and Arguments
The proposed regulations have generated a multitude of arguments, showcasing the diverse perspectives within society. Proponents emphasize the potential for improved online safety, reduced misinformation, and a more equitable digital environment. Conversely, critics worry about potential censorship, restrictions on free speech, and the chilling effect on innovation. The debate often revolves around the delicate balance between protecting users and preserving fundamental online freedoms.
Reactions from Various Sectors
Reactions to the proposed regulations differ across sectors. Tech companies, for example, often express concerns about the practical implications of the rules, such as implementation costs and potential disruptions to their services. Civil society organizations frequently highlight the importance of user rights and the potential for the regulations to negatively impact vulnerable communities. Government agencies and policymakers, on the other hand, typically focus on the benefits of the regulations for public safety and security.
Potential Consequences of Public Opposition or Support, New group sends message on internet regulation
Public opposition to the regulations could lead to significant delays in their implementation or even their complete abandonment. Conversely, strong public support could expedite the regulatory process and potentially lead to more effective enforcement. Understanding the public’s stance is crucial for the successful implementation of the proposed regulations and for addressing any potential drawbacks.
Pros and Cons of the Proposed Regulations
| Pro | Con | Perspective |
|---|---|---|
| Improved online safety and security | Potential for censorship and restrictions on free speech | Civil Liberties Groups |
| Reduced spread of misinformation and harmful content | Increased burden on tech companies for compliance | Tech Companies |
| Increased accountability for online platforms | Potential for chilling effect on innovation and creativity | Start-ups and Entrepreneurs |
| Protection of vulnerable users | Difficulty in enforcement and global application | Government Agencies |
| Enhanced transparency and accountability in online operations | Potential for unequal access to information and resources | Advocates for Digital Inclusion |
Global Context and International Cooperation
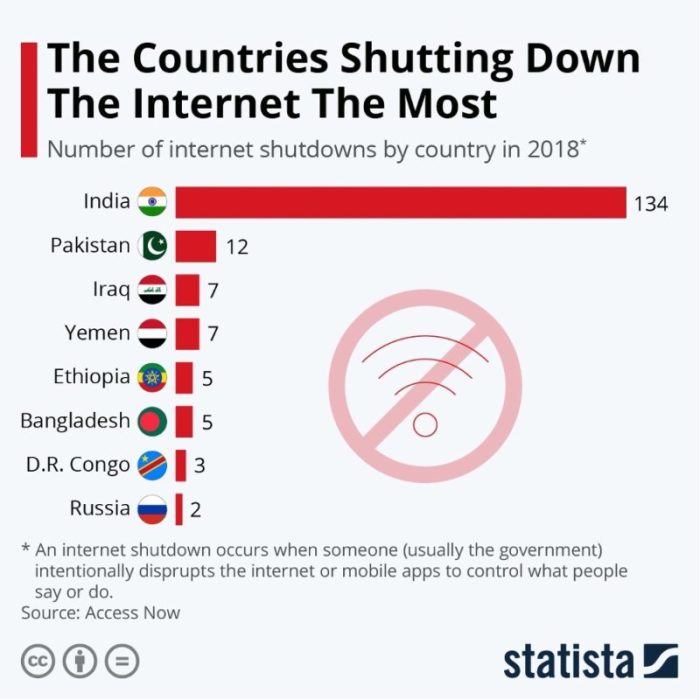
The internet’s global nature necessitates international cooperation for effective regulation. Varying cultural norms, legal systems, and technological landscapes across countries create complex challenges in establishing uniform standards. Understanding the international landscape of internet regulation is crucial for navigating the potential for both cooperation and conflict in shaping the future of the digital world.The absence of a single global authority for internet governance has led to a fragmented approach, with different countries and regions pursuing their own regulatory strategies.
This can result in inconsistencies, creating hurdles for international commerce, data exchange, and the free flow of information. Harmonizing these diverse approaches is vital for fostering a stable and predictable digital environment.
International Landscape of Internet Regulation
The international landscape of internet regulation is characterized by a multitude of actors and approaches. No single global body holds ultimate authority, but rather, a complex web of international organizations, treaties, and national laws shapes internet governance. This decentralized structure leads to challenges in achieving global consensus on critical issues.
Potential for International Cooperation or Conflict
The potential for international cooperation in internet regulation is significant. Shared concerns about cybersecurity, online safety, and the spread of misinformation can drive collaboration. However, conflicting national interests, differing cultural values, and varying levels of technological development can also lead to significant friction. Examples like the ongoing debate over data localization policies highlight the potential for conflict.
Different countries have varying approaches to data protection, leading to challenges in international data flows.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations play a critical role in shaping the international discourse on internet regulation. Organizations like the United Nations, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) provide forums for discussion and the development of best practices. These organizations foster dialogue between nations and promote a common understanding of the challenges and opportunities related to the digital world.
Key Legal Frameworks and Agreements
Several key legal frameworks and agreements shape internet governance. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights, while not directly focused on the internet, provides a foundation for discussions about freedom of expression and access to information online. The Council of Europe’s Convention on Cybercrime and other regional agreements Artikel legal frameworks for addressing specific cybercrimes. These agreements, however, often reflect national interests and priorities.
Countries’ Approaches to Internet Regulation
| Country | Approach | Legal Framework |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Market-driven approach, emphasizing freedom of speech and innovation. | Various federal and state laws, including those related to intellectual property, antitrust, and privacy. |
| China | Authoritarian approach with strict censorship and control over online content. | Cybersecurity laws and regulations, emphasizing national security and social stability. |
| European Union | Emphasis on user privacy and data protection. | General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other EU-level regulations. |
| India | Balancing economic growth with regulatory oversight. | Digital India initiative, along with various telecom and IT regulations. |
| Brazil | Focus on digital inclusion and promoting equitable access. | Specific laws and regulations pertaining to internet access and data protection. |
The table above presents a simplified overview of diverse approaches to internet regulation. Specific legal frameworks and their implementation vary widely, reflecting each nation’s unique context.
Future Trends and Projections: New Group Sends Message On Internet Regulation
The internet, once a nascent technology, has become an indispensable part of modern life. Its evolution, however, is not static. We can anticipate a dynamic future shaped by emerging technologies and societal needs, demanding a proactive approach to regulation. This section explores potential future developments in internet governance, projecting the online environment’s evolution and the implications for regulation.The future of internet regulation will be characterized by a complex interplay of technological advancements, societal pressures, and geopolitical considerations.
This intricate web of factors will drive the development of new frameworks and policies, demanding a nuanced understanding of the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Potential Developments in Internet Regulation
The internet’s ever-evolving nature necessitates constant adaptation in regulation. Anticipating and addressing future challenges is crucial for maintaining a safe, accessible, and equitable online space. Future developments are likely to focus on issues such as:
- Increased Focus on Data Privacy and Security: With the growing volume of personal data collected and stored online, regulations will likely become stricter. We can expect greater emphasis on data minimization, purpose limitation, and user control over their personal information. The recent Cambridge Analytica scandal, for example, highlighted the need for stronger data protection measures.
- Addressing the Impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI’s increasing role in online services, from content moderation to personalized recommendations, necessitates the development of regulations to mitigate potential biases, ensure transparency, and prevent misuse. AI-powered tools capable of generating realistic deepfakes are a significant concern, demanding specific regulatory frameworks to prevent misinformation and manipulation.
- Adapting to the Metaverse and Web3: The emergence of virtual worlds and decentralized technologies will require new regulatory frameworks to address issues like user verification, digital identity management, and the prevention of fraud and abuse within these new spaces. The evolving digital identity landscape needs clear guidelines.
- Addressing Global Digital Divide: Efforts to bridge the global digital divide will likely continue. This includes initiatives promoting internet access and digital literacy in underserved communities. Developing countries will need specific support in establishing robust digital infrastructure and access.
Evolution of the Online Environment
The online environment will continue to evolve, driven by new technologies and changing user expectations. This evolution will impact internet regulation significantly.
- Rise of Decentralized Technologies: Decentralized platforms and cryptocurrencies will challenge traditional centralized internet structures. This necessitates adapting regulatory frameworks to address the unique characteristics of these systems, such as the need for transparency and accountability in decentralized governance structures.
- Increased Reliance on Mobile Technology: Mobile devices will continue to dominate internet access, creating new challenges for regulatory bodies to ensure accessibility, security, and privacy on mobile platforms. The growing use of mobile devices requires tailored regulation.
- Growing Importance of Cybersecurity: As cyber threats become more sophisticated, the need for robust cybersecurity measures will be paramount. Regulation will likely focus on enhancing the resilience of online infrastructure and promoting the adoption of security best practices. This will include encouraging collaboration between governments, businesses, and researchers.
Emerging Technologies and their Impact
Emerging technologies are rapidly changing the digital landscape. This evolution requires regulators to adapt to ensure that the benefits of these technologies are realized while mitigating their risks.
- Metaverse and Virtual Reality (VR): The metaverse presents new opportunities for interaction and commerce but also new challenges for regulating user behavior, privacy, and intellectual property. New regulations will need to address the virtual world.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain’s potential for secure and transparent transactions will necessitate regulatory frameworks to address issues of anonymity, fraud prevention, and the legal status of digital assets. The evolving use of cryptocurrencies needs clear guidelines.
Illustrative Visual
Imagine a network of interconnected nodes, each representing a different aspect of the internet – users, devices, servers, and data. Lines connecting these nodes fluctuate in thickness and color, representing the dynamic flow of information. A central, slightly transparent cube represents internet governance, surrounded by a constantly shifting constellation of regulatory frameworks. This illustrates the ever-changing nature of internet governance and the need for dynamic adaptation to the ever-evolving landscape of the internet.
Alternative Approaches and Solutions
The new group’s proposed internet regulations, while aiming to address pressing concerns, may inadvertently stifle innovation and economic growth. Alternative approaches, often emphasizing collaboration and self-regulation, offer potentially more effective and less restrictive solutions. These alternative models acknowledge the complexities of the digital landscape and recognize the need for flexibility and adaptability.Exploring diverse approaches to internet regulation is crucial.
Instead of imposing rigid rules, alternative models often focus on fostering a more self-governing environment, encouraging responsible practices, and promoting digital literacy. This shift in focus prioritizes collaboration between stakeholders, empowering users, and promoting transparency.
Alternative Approaches to Internet Regulation
Various approaches exist beyond the new group’s proposed regulations. These include voluntary codes of conduct, industry self-regulation, and community-based initiatives. These approaches emphasize cooperation and shared responsibility, allowing for more dynamic adaptation to evolving challenges.
Comparison of Proposed Regulations to Alternative Approaches
| Approach | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Proposed Regulations (New Group) | Potentially addresses specific issues like misinformation and harmful content directly. Clear, centralized control. | May stifle innovation and limit free speech. Potential for overreach and inflexibility in response to rapidly changing technologies. Risk of unintended consequences. Difficulty in enforcement. |
| Voluntary Codes of Conduct | Encourages industry self-regulation and avoids heavy-handed government intervention. Can be more adaptable to evolving challenges. Focuses on fostering responsible behavior. | May lack enforcement mechanisms. Can be difficult to ensure consistent adherence. Potential for uneven application and enforcement across different platforms. |
| Industry Self-Regulation | Industry bodies can develop and enforce standards tailored to their specific needs. Greater industry expertise and understanding of technical challenges. Can adapt more rapidly to new technologies. | Potential for conflicts of interest and lack of transparency. May not effectively address issues that transcend individual platforms. Enforcement can be challenging. |
| Community-Based Initiatives | Empowers users and fosters a sense of shared responsibility. Can promote digital literacy and critical thinking. Offers flexibility and responsiveness to local contexts. | May lack widespread participation and enforcement mechanisms. Can be challenging to coordinate across different communities and regions. May struggle to address global issues. |
Examples of Alternative Solutions
The concept of “net neutrality” illustrates the tension between regulation and self-regulation. While some advocate for government oversight, others believe a more nuanced approach through self-regulation, with clear guidelines and standards enforced by industry bodies, could be more effective in the long run. A potential example would be the creation of an independent platform to adjudicate disputes and enforce codes of conduct among social media platforms, instead of a government-imposed mandate.Examples of voluntary codes of conduct in other sectors (e.g., environmental sustainability) demonstrate the potential for success with self-regulation.
These codes often Artikel shared responsibilities and expectations, promoting positive behavior and collaboration.
Potential Impact of Alternative Solutions
Alternative approaches, particularly industry self-regulation and voluntary codes of conduct, could potentially foster a more collaborative and adaptable approach to internet governance. This could lead to a more balanced approach, addressing concerns without stifling innovation. The success of these approaches hinges on strong enforcement mechanisms, clear guidelines, and ongoing dialogue between stakeholders.
Last Point
The new group’s message on internet regulation has ignited a firestorm of discussion, prompting debate across various sectors. The proposed regulations raise profound questions about the balance between freedom of expression, online safety, and economic impacts. The diverse perspectives and potential challenges associated with implementing these rules are undeniable. Ultimately, the future of internet governance will depend on how effectively the group navigates the complexities of this global debate.