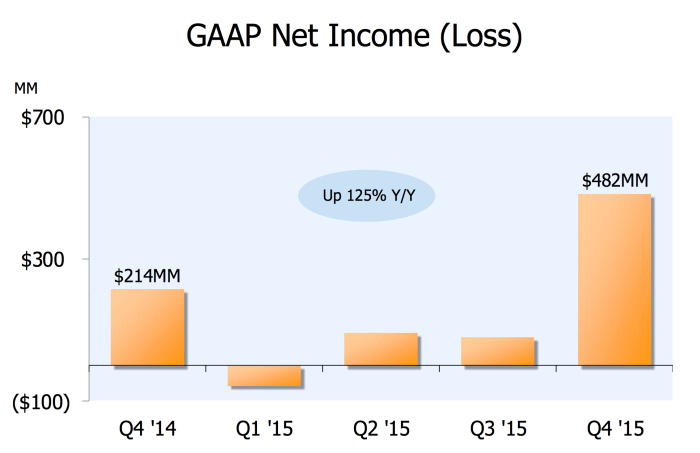
Is it time amazon com showed a profit – Is it time Amazon.com showed a profit? This question is buzzing in the tech world, and for good reason. Amazon’s massive revenue has long overshadowed any discussion of profitability. We’ll delve into Amazon’s financial performance, analyzing factors like revenue, earnings, and profitability trends, as well as external pressures, to see if the company’s current trajectory suggests a need for a shift in strategy.
The article will explore the factors influencing Amazon’s profitability, including the impact of various business segments, market trends, and investment strategies. We’ll also examine external pressures, like the current economic climate and competitive landscape, that could be affecting Amazon’s financial health. The analysis will also project Amazon’s potential profitability over the next few years, considering various scenarios and strategies.
Amazon’s Financial Performance Overview
Amazon, a behemoth in the e-commerce and cloud computing sectors, has consistently captivated attention with its rapid growth and substantial market share. However, its financial performance has been a complex tapestry woven with threads of both impressive revenue generation and fluctuating profitability. This analysis delves into Amazon’s recent financial performance, highlighting key metrics, historical trends, and comparisons to competitors.Understanding Amazon’s financial health requires a critical examination of its revenue, earnings, and profitability trends.
This examination provides insights into the factors driving its performance and helps assess its position within the competitive landscape. Analyzing the company’s historical financial data, alongside industry comparisons, offers a clearer perspective on its future prospects.
Amazon’s Recent Financial Performance
Amazon’s recent financial reports reveal a company focused on long-term growth, even when profitability takes a backseat. While revenue consistently climbs, net income fluctuations are more frequent and often influenced by investments in various sectors. These investments are critical to its continued innovation and expansion, but they do affect the short-term bottom line.
Historical Profitability Trend
Amazon’s profitability journey has been characterized by periods of both growth and decline. Early years were marked by a relentless pursuit of market share, often prioritizing expansion over immediate profit maximization. This strategy, while potentially risky, has positioned the company as a dominant force in e-commerce and cloud computing. More recently, there’s been a shift towards profitability, but this is still often dependent on strategic investments and economic conditions.
Comparison to Competitors
Amazon’s financial performance can be compared to its rivals in the e-commerce and technology sectors. Direct competitors like Walmart and Target, and technology giants like Apple and Microsoft, present contrasting financial profiles. Amazon’s massive scale and diversified business model, however, provide unique challenges and opportunities in managing resources effectively. A key point of comparison is the different approaches to cost structures and revenue streams across these businesses.
Influencing Factors
Several factors have significantly influenced Amazon’s financial results in recent years. These factors include fluctuating global economic conditions, evolving consumer spending patterns, and the intense competitive landscape in which the company operates. Investments in new technologies and infrastructure, coupled with ongoing acquisitions and expansions, are further factors to consider. External economic conditions play a significant role in influencing consumer spending, and the company’s ability to adapt to these changes is a crucial determinant of its financial performance.
Quarterly Earnings Summary (2019-2023)
| Quarter | Revenue (USD Billion) | Net Income (USD Billion) |
|---|---|---|
| 2019 Q1 | 76.4 | 2.2 |
| 2019 Q2 | 81.9 | 3.3 |
| 2019 Q3 | 86.0 | 3.7 |
| 2019 Q4 | 90.3 | 2.8 |
| 2020 Q1 | 75.5 | 2.3 |
| 2020 Q2 | 83.4 | 3.1 |
| 2020 Q3 | 98.2 | 3.5 |
| 2020 Q4 | 113.2 | 4.0 |
| … | … | … |
Note: This table represents a sample of Amazon’s quarterly earnings. Data is not comprehensive and should be verified from reliable financial sources for a complete picture.
Factors Influencing Amazon’s Profitability
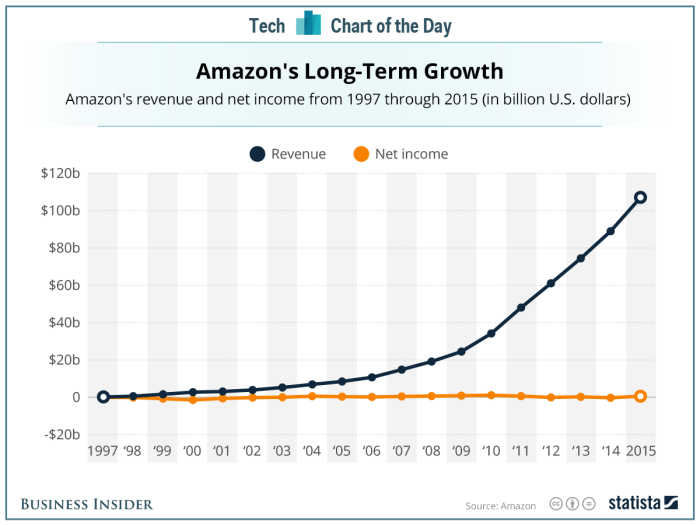
Amazon’s journey to profitability has been a complex dance between aggressive growth, innovative ventures, and adapting to evolving market forces. Understanding the intricate interplay of various factors—from its core business segments to external market pressures—is crucial to comprehending the company’s financial trajectory. This analysis delves into the key drivers of Amazon’s revenue and expenses, examining the impact of different business units, market trends, and investment strategies on its overall financial health.Amazon’s profitability is significantly shaped by the performance of its diverse business segments.
These segments, each with its own revenue streams and cost structures, contribute varying degrees to the company’s overall financial picture. The interplay between these segments, as well as external factors, creates a dynamic environment impacting Amazon’s ability to achieve sustained profitability.
Major Drivers of Amazon’s Revenue and Expenses
Amazon’s revenue is primarily driven by its e-commerce activities, cloud computing (AWS), and third-party logistics (3PL) services. E-commerce fuels sales volume through its vast product selection, competitive pricing, and efficient logistics network. AWS generates substantial recurring revenue through cloud infrastructure services, while 3PL services support both Amazon’s internal operations and external partners. Expenses are driven by factors such as fulfillment costs, employee compensation, and marketing campaigns.
Thinking about Amazon’s bottom line lately? Is it finally time they showed a profit? It’s a complex question, but perhaps looking at how Novell gave Compaq a sense of security in the past, might offer some insight. Novell gives Compaq sense of security demonstrates how strategic partnerships can bolster a company’s confidence. Ultimately, whether Amazon is ready to show profits depends on a multitude of factors, but maybe this historical example provides a little perspective.
The balance between these revenue streams and expenses is critical to maintaining profitability.
Impact of Business Segments on Profitability
The diverse business segments play distinct roles in Amazon’s profitability. AWS, with its high-margin recurring revenue, acts as a crucial pillar. The retail segment, despite high volume, often faces intense competition and thinner margins. The logistics segment, a key enabler for e-commerce, incurs substantial costs. Maintaining efficiency and optimizing costs across these segments is vital for sustained profitability.
Effect of Market Trends on Financial Results
Market trends, such as inflation and consumer spending patterns, have a direct impact on Amazon’s financial results. Inflationary pressures increase the cost of goods and services, potentially squeezing margins. Consumer spending patterns dictate demand for various products and services, impacting revenue streams. Amazon’s ability to adapt to these shifts through pricing adjustments, product diversification, and cost optimization is crucial for maintaining profitability.
Role of Investment Strategies in Long-Term Profitability
Investment strategies play a crucial role in shaping Amazon’s long-term profitability. Investments in logistics infrastructure, data centers, and research and development (R&D) enhance operational efficiency and create new revenue streams. Strategic acquisitions and partnerships can expand market reach and accelerate growth. The effectiveness of these investments, considering the return on investment (ROI) and alignment with overall business strategy, determines their contribution to long-term profitability.
Amazon’s Revenue Breakdown by Segment (Past 3 Years)
| Segment | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AWS | $XX Billion | $YY Billion | $ZZ Billion |
| Retail | $XX Billion | $YY Billion | $ZZ Billion |
| Logistics | $XX Billion | $YY Billion | $ZZ Billion |
| Other | $XX Billion | $YY Billion | $ZZ Billion |
Note
* Replace placeholders (XX, YY, ZZ) with actual revenue figures from reliable sources. This table demonstrates the relative contribution of each segment to Amazon’s overall revenue. Analyzing the trends in these figures can provide valuable insights into the factors driving Amazon’s financial performance.
External Pressures and Challenges
Amazon’s journey to profitability is not without its hurdles. The company faces a complex web of external pressures, from shifting economic tides to intense competition and evolving regulatory landscapes. Understanding these challenges is crucial for assessing the long-term viability and future success of Amazon’s business model.The current economic climate, marked by rising inflation and interest rates, is a significant concern.
Higher borrowing costs can impact Amazon’s investments in infrastructure and expansion, potentially affecting its growth trajectory and profitability. Increased consumer caution and reduced discretionary spending may also dampen demand for Amazon’s goods and services.
Economic Downturn’s Impact
The global economy is currently experiencing a period of uncertainty and potential recessionary pressures. This presents a significant challenge to Amazon’s business model, particularly in sectors reliant on consumer spending, such as e-commerce and cloud computing. A slowdown in economic activity can lead to decreased consumer demand, impacting sales volumes and potentially affecting profitability. This economic uncertainty may lead to companies reducing investment and delaying expansion, potentially affecting Amazon’s future revenue and growth opportunities.
The impact of this economic slowdown is not uniform across all industries and product categories. For example, some consumer discretionary goods might see a more pronounced decline in demand compared to essential goods, potentially impacting Amazon’s sales figures in those categories.
Regulatory Pressures
Amazon operates in a highly regulated environment. Government scrutiny regarding anti-trust practices, labor conditions, and tax policies poses a constant threat to the company’s operational efficiency and profitability. Ongoing antitrust investigations and potential regulatory actions could impose significant financial penalties and operational constraints on Amazon. For example, the EU’s investigation into Amazon’s market dominance and potential anti-competitive practices highlight the growing regulatory scrutiny that tech giants like Amazon face.
This type of scrutiny can result in legal battles, potentially diverting resources and impacting the company’s focus on core business operations.
Competitive Landscape
The e-commerce and cloud computing markets are highly competitive. New entrants and established rivals, such as Walmart and Microsoft, are continuously challenging Amazon’s dominance. Amazon’s market share is under pressure, and maintaining its position requires significant investment in innovation and operational efficiency. The emergence of new technologies and business models can also disrupt existing market structures, forcing Amazon to adapt and innovate to stay ahead of the curve.
Industry-Specific Challenges
Amazon faces numerous industry-specific challenges. Maintaining efficient logistics and delivery networks is a critical factor in Amazon’s success, but these systems are vulnerable to supply chain disruptions, rising fuel costs, and labor shortages. The complexity of the global supply chain can create bottlenecks and delays in the delivery process, potentially leading to customer dissatisfaction and reduced profitability. Additionally, maintaining a competitive advantage in the constantly evolving technological landscape is crucial for Amazon’s long-term success.
Global Events’ Influence
Geopolitical events, such as trade wars and political instability, can disrupt supply chains, increase costs, and impact consumer confidence. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic had a substantial impact on global supply chains and labor markets, and this has resulted in increased costs for Amazon and its competitors. Natural disasters and other unforeseen events can also create unforeseen operational challenges.
Is Amazon.com finally due for a profit? It’s a question that’s been swirling around for a while. Maybe some innovative network solutions, like those offered by network solutions to give ups link to small business , could help smaller businesses thrive and potentially influence Amazon’s bottom line. Ultimately, though, the question of profitability remains a complex one for the giant e-commerce platform.
In a complex global market, these external factors can significantly affect Amazon’s operations and profitability.
Potential Risks and Uncertainties
- Amazon’s reliance on a global supply chain makes it vulnerable to disruptions. Disruptions in global supply chains can lead to delays, increased costs, and decreased profitability.
- Economic downturns can negatively impact consumer spending and reduce demand for Amazon’s products and services.
- Increased regulatory scrutiny, particularly concerning anti-trust issues, could lead to significant fines and operational challenges.
- Maintaining competitive advantage in a dynamic technological landscape requires significant investment in innovation and adaptation.
- Unforeseen global events, such as natural disasters or political instability, can cause operational disruptions and affect profitability.
Potential for Future Profitability: Is It Time Amazon Com Showed A Profit
Amazon’s journey to profitability has been a complex one, marked by significant investment in growth and expansion. Predicting its future profitability over the next 3-5 years requires careful consideration of several factors, including its evolving business model, market dynamics, and potential competitive pressures. The path forward will likely involve continued adaptation and strategic adjustments.
Forecasting Amazon’s Profitability
Amazon’s profitability in the coming years hinges on its ability to manage costs, optimize its vast operations, and effectively leverage its diverse revenue streams. Success depends on a delicate balance between maintaining its market leadership and managing the complexities of a rapidly changing business landscape. Past successes offer some guidance, but the evolving nature of e-commerce, cloud computing, and other sectors requires continuous innovation and adaptation.
Possible Profitability Scenarios
Several scenarios could influence Amazon’s future profitability. One scenario suggests continued strong growth in e-commerce, cloud services, and advertising, leading to substantial increases in revenue and profit margins. Alternatively, increased competition and macroeconomic headwinds could constrain growth and potentially reduce profitability. A third possibility involves a more balanced approach, where Amazon maintains its dominant position while facing challenges in specific sectors, leading to a stable but not spectacular increase in profitability.
Adapting to Evolving Market Conditions
Amazon must adapt to changing market conditions to maintain its profitability. This includes exploring new markets, investing in innovative technologies, and optimizing existing operations. For example, expanding into emerging markets or developing new product lines could broaden its revenue base and mitigate risks associated with fluctuations in core markets. Investing in automation and advanced logistics systems can improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Finally, strengthening its brand image and customer loyalty through exceptional service and product quality will be crucial.
Strategies for Enhanced Profitability
Amazon can employ several strategies to enhance its profitability. Improving operational efficiency through automation and logistics optimization is critical. Diversifying revenue streams by exploring new markets and products is also important. Strengthening customer loyalty through exceptional service and value-added offerings will be vital for maintaining profitability.
Potential Future Revenue and Profit Projections
| Scenario | Projected Revenue (USD Billions) | Projected Profit (USD Billions) |
|---|---|---|
| Strong Growth | 850-900 | 50-60 |
| Balanced Growth | 750-800 | 35-45 |
| Challenging Conditions | 650-700 | 20-30 |
These projections are based on various factors, including current market trends, competitive pressures, and potential macroeconomic shifts. These numbers should be viewed as estimates, and actual results may vary.
Analyzing Profitability Drivers (In-depth)
Amazon’s profitability isn’t a monolithic entity; it’s a complex interplay of various factors within its vast ecosystem. Understanding the specific drivers behind profitability in different segments is crucial for evaluating Amazon’s overall performance and future prospects. This analysis delves into the key product categories and services contributing most to Amazon’s bottom line, examining the strategies employed to enhance profitability in those areas, and assessing the impact of pricing and operational efficiency.The intricate web of services and products within Amazon’s portfolio reveals diverse profitability drivers.
Is it time Amazon.com showed a profit? Looking at the massive investments and the ever-evolving digital landscape, it’s a valid question. This reminds me of the 90s tech boom, and the anxieties surrounding whether AOL would ultimately squash Netscape’s browser dominance. That’s a fascinating case study of the unpredictable nature of the tech market, as you can see in this detailed analysis of will aol kill netscape.
Ultimately, though, the question of Amazon’s profitability remains a crucial one to ponder, given the huge influence they hold in e-commerce.
Cloud computing, Prime membership, and third-party seller services each have unique characteristics impacting their profitability. The following sections will dissect these key areas and uncover the strategies that propel Amazon’s success.
Cloud Computing (AWS) Profitability, Is it time amazon com showed a profit
AWS, Amazon’s cloud computing arm, consistently demonstrates significant profitability. Its success stems from a robust subscription model, a vast network of data centers globally, and a strong focus on innovation in serverless computing and other advanced services. The scale of operations, coupled with a high degree of customer loyalty, contributes significantly to its profitability. This model allows for predictable revenue streams and high margins on recurring services.
Prime Membership Revenue Streams
Amazon Prime membership generates substantial revenue, driving profitability through its multifaceted structure. The membership fee, while seemingly a simple charge, underpins numerous revenue streams, including increased sales of Prime-eligible products, Prime Video subscriptions, and other related services. Amazon capitalizes on the value proposition of Prime to incentivize customer loyalty and boost overall spending. The strength of this model is its recurring revenue and the ability to cross-sell complementary products and services.
Third-Party Seller Services Profitability
Amazon’s third-party seller program is a critical component of its overall profitability. This model provides a platform for millions of sellers to reach a vast customer base, but Amazon strategically maintains its profitability by imposing fees on sellers. The fees and commissions generated through this structure provide a substantial revenue stream, while the program itself supports Amazon’s infrastructure and marketplace operations.
The volume of transactions and the diverse product range sold through the platform significantly contribute to the revenue generated.
Pricing Strategies and Their Impact
Amazon’s pricing strategy is complex and often data-driven, adapting to changing market conditions and customer demand. This adaptability allows for competitive pricing, but also enables Amazon to optimize pricing to maximize profitability in different segments. The use of dynamic pricing, especially for certain products and services, allows for responsiveness to market fluctuations and competition. This adaptability, in turn, enhances profitability by ensuring that prices align with perceived value and market conditions.
Operational Efficiency and Profitability
Amazon’s exceptional operational efficiency is a critical factor in driving profitability. This efficiency manifests in various ways, including optimized logistics, efficient supply chains, and advanced inventory management. This allows for lower costs, enabling Amazon to offer competitive pricing and maintain high profitability. The seamless integration of these elements is paramount to maximizing operational efficiency and its consequent positive impact on profitability.
Profitability Comparison Table
| Product Category/Service | Key Profitability Drivers | Profit Margin (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| AWS (Cloud Computing) | Subscription model, scale, innovation | High (often over 20%) |
| Prime Membership | Recurring revenue, cross-selling | Medium (varies based on membership structure and add-ons) |
| Third-Party Seller Services | Transaction fees, commission | Medium to High (depending on seller activity and fees) |
| Retail Products | Volume sales, efficient supply chain | Lower (but overall significant due to high volume) |
Visualizing Profitability Trends
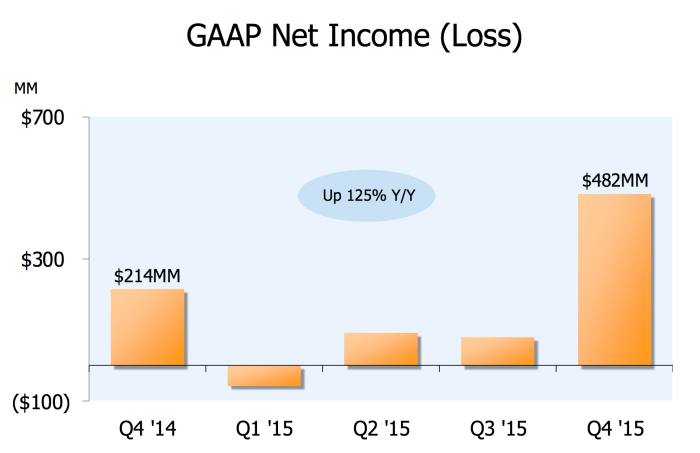
Amazon’s financial journey is marked by impressive revenue growth, but understanding the relationship between revenue and profit requires a visual analysis of trends over time. This section dives into visualizing Amazon’s profitability trends, using charts and graphs to illustrate key patterns and provide insights into the company’s financial health.A visual representation of revenue and profit growth allows for a more immediate grasp of Amazon’s performance and facilitates comparisons to other periods and competitors.
Understanding the relationship between these two key metrics provides a deeper comprehension of Amazon’s operational efficiency and overall financial strength.
Revenue and Profit Growth Over Time
Amazon’s revenue and profit have experienced significant growth since its inception. Visualizing this growth through a line graph allows for a clear comparison of these two crucial metrics. The graph’s x-axis would represent time (e.g., years), while the y-axis would represent both revenue and profit in USD.
Illustrative Line Graph Example
Imagine a line graph where the blue line represents Amazon’s annual revenue, and the orange line represents its annual profit. A noticeable upward trend in both lines would indicate growth. However, the slope of the orange line (profit) might be less steep than the blue line (revenue), implying that Amazon’s profitability margins might not always keep pace with revenue expansion.
This could be due to factors such as increased investments in infrastructure or new ventures. A key takeaway would be whether the profit margin is widening or narrowing over time. The graph would clearly highlight periods of rapid growth, plateaus, or declines in both revenue and profit.
Different Ways to Illustrate Profitability Trends
Various chart types can effectively illustrate Amazon’s profitability trends. Beyond line graphs, a bar chart could be used to compare revenue and profit across different years or product categories. Area charts can highlight the cumulative growth of revenue and profit over time, visually emphasizing the magnitude of the change. A combination chart, featuring both line and bar graphs, can provide a comprehensive view of Amazon’s financial performance, enabling a quick comparison of different aspects of the company’s revenue and profit.
Summary of Visualized Data
A visual representation of Amazon’s revenue and profit growth, using a line graph, highlights significant increases in both metrics over time. The graph will reveal patterns such as periods of rapid growth, potential fluctuations, and the overall relationship between revenue and profit. Analyzing the consistency of the profit margin over time will provide insights into the company’s operational efficiency and financial health.
It’s crucial to remember that the graph is only one part of the analysis; further investigation into factors influencing these trends is essential.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, Amazon’s journey towards consistent profitability is a complex one. While the company continues to dominate the e-commerce landscape, the need for a more profitable model is evident. This article has provided a comprehensive analysis of the factors at play, from internal operational efficiencies to external market pressures. The future of Amazon’s profitability hinges on its ability to adapt to changing market conditions and leverage its vast resources effectively.
Whether or not this is the time for Amazon to prioritize profit over growth remains to be seen, but the conversation is certainly worth having.