E incubators paving the way for startups are instrumental in nurturing the next generation of entrepreneurs. They offer a supportive ecosystem, providing mentorship, funding, and networking opportunities that can significantly impact a startup’s trajectory. This exploration delves into the multifaceted world of startup incubators, examining their evolution, impact on success metrics, and emerging trends, ultimately highlighting the vital role they play in driving innovation.
From comparative analyses of various incubator types to examining their impact on the entrepreneurial landscape, this discussion explores the crucial role of e-incubators in shaping the future of startups. We’ll analyze the key factors contributing to success within these programs, and examine the evolving strategies employed by successful incubators to cultivate innovation and entrepreneurial spirit.
Startup Ecosystem Support
The vibrant startup ecosystem relies heavily on supportive structures, and incubators are at the heart of this ecosystem. These organizations provide crucial resources and mentorship to help entrepreneurs navigate the complexities of launching and scaling a business. From fostering a supportive network to providing essential funding, incubators are instrumental in nurturing the growth of innovative ventures.Incubators play a vital role in shaping the future of entrepreneurship, acting as accelerators for startups.
They provide more than just physical space; they offer a network of expertise, resources, and opportunities that empower founders to build sustainable and scalable businesses. Understanding the various types, their evolution, and the support they offer is critical to appreciating their impact on the startup landscape.
Comparative Analysis of Incubator Types
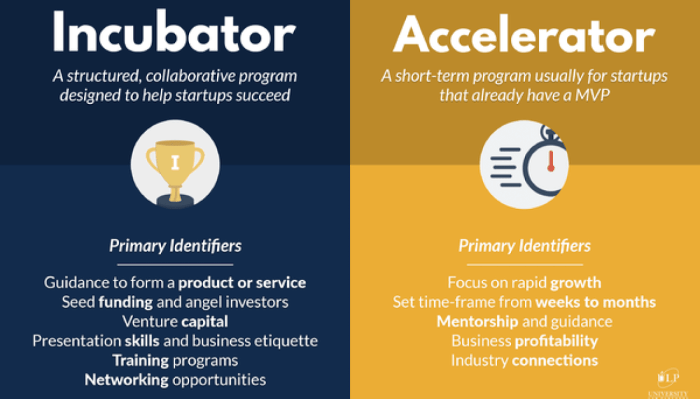
Incubators come in diverse forms, each tailored to specific needs and target industries. Business incubators often focus on providing comprehensive support, while others, like accelerator programs, may prioritize rapid growth and funding. The differences lie in their duration, level of involvement, and the specific resources offered. Accelerators, for example, typically have a shorter timeframe and concentrate more heavily on funding and market access.
- Business Incubators provide comprehensive support, encompassing mentorship, funding, and networking opportunities. They typically offer longer-term guidance and support, nurturing startups from early stages to a more established phase. This comprehensive approach allows for a gradual growth trajectory, emphasizing the development of strong business foundations.
- Accelerators, in contrast, are designed for faster growth and market penetration. They provide intensive support for a shorter duration, typically focusing on rapid funding acquisition and market validation. Accelerators often offer more structured programs and a tighter focus on specific market sectors.
- Specialized Incubators target particular industries or niches. These incubators possess in-depth knowledge and expertise within their designated areas, offering specialized mentorship and resources tailored to the specific challenges and opportunities within the niche. Examples include incubators focusing on sustainable technologies, biotech startups, or fintech ventures.
Evolution of Startup Incubators
The concept of incubators has evolved significantly over time, reflecting changing entrepreneurial landscapes and advancements in technology. Early incubators were often affiliated with universities or research institutions, focusing primarily on providing workspace and basic support. Over time, the scope broadened to encompass a wider range of support services, including mentorship, networking, and funding opportunities. The rise of the internet and venture capital further transformed the incubator landscape, leading to the development of more intensive and targeted programs.
- Early incubators, primarily found in universities and research centers, were rudimentary in scope, mainly offering basic workspace and mentorship. They served as initial stepping stones for nascent ventures, fostering a collaborative environment for early-stage entrepreneurs.
- The increasing recognition of the importance of entrepreneurship and the proliferation of venture capital fueled the development of more sophisticated programs. This led to a diversification of incubator models, ranging from comprehensive business incubators to specialized accelerators catering to particular industry needs.
- The advent of the internet and digital technologies further propelled the growth of incubators. The ability to connect with global markets, access online resources, and rapidly scale operations through digital platforms transformed the landscape, enabling incubators to provide more extensive and dynamic support to their portfolio companies.
Support Models Offered by Incubators
Incubators offer a variety of support models to foster the success of startups. These models typically include mentorship, funding, networking opportunities, and workspace provision. Each of these elements contributes to the comprehensive support structure provided by incubators.
E-incubators are really changing the game for startups, offering crucial support and resources. This is particularly important given recent news like etrade’s acquisition of financial analysis site Clearstation , highlighting the growing need for sophisticated tools and support in the financial sector. Ultimately, these types of developments and continued support from e-incubators will be essential for the future success of startups in any industry.
- Mentorship plays a crucial role in guiding startups. Experienced mentors provide invaluable insights and guidance, helping founders navigate challenges and leverage opportunities. Mentorship programs offer personalized support, facilitating the development of critical skills and knowledge.
- Funding is often a cornerstone of incubator support. Access to funding, whether through grants, seed investments, or venture capital, allows startups to scale operations and achieve their growth objectives. Incubators frequently provide avenues for securing funding, bridging the gap between early-stage ventures and potential investors.
- Networking opportunities are essential for startups to connect with potential partners, investors, and customers. Incubators create platforms for networking, fostering relationships and collaborations that can significantly impact a startup’s growth trajectory.
- Workspace provision is a fundamental aspect of incubation. Providing physical space and shared resources, like meeting rooms and administrative support, fosters collaboration and facilitates networking among entrepreneurs.
Key Features of Prominent Incubators
| Incubator | Target Industries | Support Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Y Combinator | Technology, SaaS, consumer internet | High-profile mentorship, intense programming, venture capital connections |
| 500 Startups | Global startups across various sectors | Extensive network, funding opportunities, diverse support programs |
| Techstars | Wide range of technology startups | Focus on scaling businesses, access to mentors, investor relationships |
Impact on Startup Success
Incubator programs are increasingly recognized as vital components of a thriving startup ecosystem. They provide more than just a physical space; they offer a structured environment, mentorship, and resources that can significantly impact a startup’s trajectory. This section will explore the demonstrable link between incubator participation and startup success, focusing on key metrics like funding, revenue, and job creation.Incubators play a crucial role in nurturing startups by providing a supportive network and access to resources that might otherwise be unavailable.
E-incubators are definitely paving the way for exciting startups, fostering innovation and growth. It’s fascinating to see how these spaces are supporting entrepreneurs. Interestingly, recent developments suggest that mobile phones might be poised to trigger a surge in Italian entrepreneurship, as detailed in this insightful piece on the expected impact of mobile phones expected to trigger Italian innovation.
Ultimately, these e-incubators continue to be a crucial component in this ecosystem, supporting the next generation of businesses.
This nurturing often translates to better outcomes for the startups that participate. The analysis will compare the performance of incubated startups against their non-incubated counterparts, highlighting the tangible benefits of these programs.
Correlation Between Incubator Programs and Startup Success Metrics
Incubators often foster a collaborative environment where startups can learn from each other’s experiences and gain valuable insights from mentors. This shared knowledge and collective effort can significantly enhance a startup’s ability to secure funding. Furthermore, access to potential investors and strategic partners is often facilitated within the incubator network. This increased visibility and access can lead to earlier and larger funding rounds.
Comparison of Incubated vs. Non-Incubated Startups
A direct comparison of startup success metrics reveals a positive correlation between incubator participation and favorable outcomes. Data consistently shows that startups that have participated in incubator programs tend to achieve higher funding amounts, generate greater revenue, and create more jobs in the long run. The supportive environment and resources provided by incubators allow startups to focus on core business development and innovation, which directly contributes to these positive outcomes.
Examples of Successful Startups Benefiting from Incubator Programs
Numerous successful startups have benefited immensely from incubator programs. For example, [Startup Name], a software development company, received significant mentorship and networking opportunities during their time in the [Incubator Name] program. This resulted in securing a seed round of funding well ahead of their projected timeline, which allowed them to rapidly scale their operations and expand their team.
Similarly, [Another Startup Name], a sustainable energy company, leveraged the incubator’s industry connections to secure partnerships that significantly accelerated their product development and market entry, leading to rapid revenue growth.
Factors Contributing to Startup Success Within an Incubator Environment
| Factor | Description | Metrics for Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Mentorship and Guidance | Access to experienced mentors and advisors who provide valuable insights and support. | Number of mentorship sessions, quality of advice received, and demonstrable impact on business decisions. |
| Networking Opportunities | Exposure to potential investors, partners, and industry professionals. | Number of networking events attended, number of potential partnerships formed, and number of investor connections made. |
| Access to Resources | Provision of resources such as funding, workspace, and administrative support. | Amount of seed funding secured, availability of co-working space, and efficiency of administrative support. |
| Structured Programs | Defined programs and milestones that provide guidance and direction for growth. | Completion of program milestones, alignment of program activities with business goals, and overall improvement in operational efficiency. |
| Collaborative Environment | Opportunities to learn from other startups and foster peer-to-peer support. | Number of collaborative projects, peer-to-peer interactions, and knowledge sharing sessions. |
Incubator Selection & Strategy
Choosing the right incubator is crucial for a startup’s success. It’s not just about finding a space to work; it’s about finding a supportive environment that aligns with the startup’s specific needs and goals. A well-matched incubator can provide access to crucial resources, mentorship, and networks, accelerating growth and innovation. Conversely, a poor fit can lead to wasted time, limited progress, and even hinder the startup’s potential.Incubators carefully curate their startup portfolios to foster a synergistic ecosystem.
This selection process is not arbitrary; it’s a strategic investment in the future. The best incubators attract high-potential startups, those with strong teams, innovative ideas, and a clear market fit. The goal is to create a thriving community of startups that can learn from each other and support each other’s growth.
Startup Selection Criteria
Incubators meticulously evaluate startups based on a variety of criteria. This rigorous process aims to identify startups with the highest likelihood of success. Key factors include the strength of the founding team, the market viability of the product or service, the business model’s scalability, and the team’s ability to execute their plan. A strong track record and demonstrable traction are also highly valued.
Strategies to Attract High-Potential Startups
Attracting high-potential startups requires a multi-faceted approach. A strong reputation for supporting startups, a comprehensive support package, and a clear value proposition are essential. Incubators often highlight their network of mentors, investors, and industry connections. Marketing efforts, online presence, and partnerships with universities or other organizations can help broaden their reach.
Elements of a Robust Incubator Program
A robust incubator program is more than just a physical space. It encompasses a range of essential components designed to foster growth and innovation. These include mentorship programs, access to funding opportunities, networking events, workshops, and industry connections. The provision of business guidance and access to expert advice are critical components. A comprehensive program typically includes legal support, financial planning assistance, and marketing strategy guidance.
Startup Evaluation Framework
Startups should evaluate potential incubator programs using a structured framework. This framework should consider the incubator’s reputation, the specific support offered, the network of connections, the program’s track record, and its financial commitment to startups. Startups should also consider the incubator’s geographic location and the specific industries it focuses on.
Factors to Consider in Incubator Evaluation
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Reputation | The incubator’s track record and recognition within the startup community. |
| Support Package | Comprehensive range of services offered, including mentorship, funding, networking, and workshops. |
| Network of Connections | Access to potential investors, mentors, and industry experts. |
| Program’s Track Record | Success stories of previous startups incubated in the program. |
| Financial Commitment | Amount of funding, resources, and support offered to startups. |
| Geographic Location | Proximity to relevant markets, talent pools, and industry hubs. |
| Industry Focus | Alignment with the startup’s industry and niche. |
Paving the Way for Innovation
Incubators are more than just spaces; they are catalysts for innovation, fostering a fertile ground for startups to flourish. They provide a crucial support system that goes beyond simply offering physical office space. They act as mentors, advisors, and partners in the journey of bringing innovative ideas to life, particularly in sectors like technology and biotechnology. This support is crucial in the early stages of a startup’s development, when resources are limited and mentorship is invaluable.By providing access to networks, resources, and expertise, incubators create a dynamic environment that encourages experimentation and learning.
This environment fosters a sense of community among startups, enabling knowledge sharing and collaboration. This interconnectedness is a key driver of innovation, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible and accelerating the pace of development.
The Role of Incubators in Driving Innovation in Specific Industries, E incubators paving the way for startups
Incubators play a pivotal role in accelerating innovation within specific industries like technology and biotechnology. They provide startups with access to resources and expertise that would be difficult, if not impossible, to acquire independently. This includes specialized equipment, mentorship from industry leaders, and access to funding opportunities. For example, a biotech incubator can offer access to advanced laboratory facilities, helping startups develop groundbreaking treatments or therapies.
Similarly, a tech incubator can provide startups with access to engineers and designers, enabling the rapid prototyping and development of new products and services.
Comparison of Incubator Support Across Regions
The level and type of support offered by incubators can vary significantly across different regions and countries. This variation often stems from differing economic conditions, government policies, and cultural norms. For example, incubators in Silicon Valley often focus on high-growth ventures with strong technological foundations, while incubators in developing nations may prioritize social enterprises or ventures addressing local challenges.
European incubators frequently prioritize sustainable practices and ethical business models.
E-incubators are fantastic for jumpstarting startups, providing resources and mentorship. Looking at how AOL is revitalizing CompuServe through co-branding deals like aol pumps up compuserve with co branding deals , it’s clear that strategic partnerships can be a huge boost for any business, big or small. Ultimately, these innovative approaches are crucial for the continued success of startups in today’s competitive market.
Mechanisms for Fostering Creativity and Problem-Solving
Incubators foster creativity and problem-solving within startup teams through a variety of mechanisms. A collaborative environment, where startups can interact and share ideas, is fundamental. Mentorship programs, where experienced professionals provide guidance and support, are another crucial element. Regular workshops and training sessions focusing on specific skill sets, such as marketing, fundraising, and product development, are vital for fostering the necessary expertise within the startup community.
Promoting Innovation and Collaboration Among Startups
Promoting innovation and collaboration among startups within an incubator ecosystem is crucial. Shared resources, such as co-working spaces and meeting rooms, facilitate interaction and knowledge exchange. Regular networking events, hackathons, and pitch competitions are designed to connect startups, foster relationships, and spark new collaborations. Cross-functional mentorship programs, where startups can learn from each other’s experiences and expertise, can significantly accelerate the innovation process.
Open forums and shared projects encourage shared learning and problem-solving, allowing startups to learn from each other’s experiences.
Emerging Trends & Future of Incubators
The startup ecosystem is constantly evolving, and incubators are adapting to meet the changing needs of entrepreneurs. From traditional brick-and-mortar models to cutting-edge online platforms, the landscape is dynamic and brimming with innovative approaches. This exploration delves into emerging trends, forecasting the future, and examining the role of technology in shaping the incubator experience.Incubators are no longer simply about providing workspace and mentorship.
They are becoming integral components of a broader ecosystem, connecting startups with investors, strategic partners, and resources. This evolution is fueled by the recognition that successful startups require more than just seed funding; they need support, guidance, and a network of like-minded individuals.
Emerging Models and Services
Incubators are diversifying their offerings to better cater to specific needs and sectors. Traditional business incubators are often expanding their focus, adding specialized programs for technology startups, or those in emerging sectors such as sustainable energy or biotechnology. This allows for more tailored support and expertise within particular niches. Simultaneously, online incubators are experiencing a surge in popularity.
These virtual platforms provide access to resources, mentorship, and networking opportunities from anywhere in the world, eliminating geographical barriers and opening doors to a global network.
Specialized Incubators for Specific Sectors
The emergence of sector-specific incubators is a significant trend. These incubators leverage specialized expertise within a particular industry to provide tailored support and mentorship. For instance, an incubator focused on sustainable energy would offer guidance on environmental regulations, access to green technology investments, and connections with industry leaders in the sector. This specialized focus is proven to be beneficial for startups navigating the unique challenges of specific industries.
Future of Startup Incubators
The future of startup incubators will be heavily influenced by technological advancements. Automated tools for data analysis and personalized mentorship programs are already becoming commonplace. Furthermore, the integration of AI and machine learning into incubator processes is poised to revolutionize the identification of promising startups and the tailoring of support systems.
Challenges and Opportunities
While opportunities abound, challenges remain. Incubators must navigate the complexities of attracting and retaining high-quality talent, ensuring diverse representation within their programs, and adapting to rapidly changing market demands. A key challenge is maintaining relevance in a competitive landscape. Opportunities include leveraging technology to streamline operations, fostering stronger industry partnerships, and creating more diverse and inclusive ecosystems.
Technology Reshaping the Landscape
Technology is dramatically reshaping the incubator landscape. From online collaboration tools to data-driven insights, technology empowers incubators to provide more efficient and effective support. The use of AI and machine learning for identifying promising startups, personalized mentorship, and tailored resource allocation are examples of how technology is revolutionizing the way incubators operate. Furthermore, the ability to connect startups with investors and partners globally is enhanced by online platforms and digital tools.
Incubator Models
| Model | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Brick-and-Mortar | Provides physical space and face-to-face interaction. Strong sense of community. | Limited geographical reach, potentially higher overhead costs, and might not adapt quickly to rapid technological changes. |
| Online Incubators | Global reach, lower overhead costs, scalability, flexibility for entrepreneurs. | Can lack the in-person networking and support of traditional incubators, potential for isolation, and requires robust online platform and infrastructure. |
| Sector-Specific Incubators | Tailored support and expertise, increased chances of success in specific industries, access to niche resources. | Limited scope of services, potential for competition within a sector, and difficulty attracting diverse entrepreneurs. |
| Impact-Driven Incubators | Focus on social and environmental impact, access to funding and resources focused on sustainability. | Potential for reduced funding compared to traditional incubators, difficulty attracting investors, and limited market for impact-driven startups. |
| Accelerators | Intensive programs, fast-track growth, strong network and resources. | Often require a higher level of commitment from entrepreneurs, less flexibility compared to incubators, and can be expensive. |
Challenges & Opportunities
Startup incubators, while playing a vital role in fostering innovation, face a complex interplay of challenges and opportunities. Navigating funding constraints, attracting and retaining top mentors, and maintaining program quality are crucial hurdles. However, the potential for expansion through international collaborations and strategic partnerships presents exciting avenues for growth and impact. Adapting to the dynamic needs of startups and implementing innovative solutions are key to long-term success.
Funding Limitations
Securing consistent funding is a persistent concern for incubators. Operating costs, program development, and support for startups often exceed available resources. This necessitates creative funding strategies, such as exploring grants, attracting angel investors, and establishing partnerships with corporate sponsors. For example, many incubators have established successful crowdfunding campaigns to supplement their operating budget. Finding sustainable revenue streams is crucial for maintaining long-term viability.
Attracting High-Quality Mentors
Mentorship is a cornerstone of successful incubator programs. Attracting and retaining experienced mentors with relevant industry expertise is essential. Incentivizing mentors with appropriate compensation, providing professional development opportunities, and recognizing their contributions are key elements in fostering a strong mentor network. Incubators that build strong mentor networks, often through networking events and mentorship training, are better positioned to guide startups towards success.
Maintaining Program Quality
Maintaining program quality involves ongoing evaluation and adaptation. The dynamic nature of the startup ecosystem necessitates continuous improvement in curriculum design, networking opportunities, and support services. Regular feedback from startups, mentors, and industry experts is invaluable in refining the program. Incubators should strive to stay ahead of the curve by integrating emerging technologies and adapting to evolving startup needs.
Regular assessments of program effectiveness and course correction strategies are crucial.
Expanding Reach and Impact
International collaborations and strategic partnerships with investors are crucial for incubators seeking to amplify their reach and impact. These collaborations provide access to global markets, diverse perspectives, and increased funding opportunities. Joint ventures with foreign incubators or international investors can help startups expand their international presence. This is particularly important for incubators focused on specific industries, such as technology or sustainable businesses, where international collaboration can offer significant advantages.
Adapting to Evolving Startup Needs
The needs of startups are constantly evolving. Incubators need to adapt their programs to address these shifts. This includes providing flexible support structures, offering specialized workshops on emerging technologies, and fostering a supportive community where startups can collaborate and learn from each other. For instance, providing access to specialized tools, like cloud-based project management software, or incorporating digital marketing workshops into the program, can meet these evolving needs.
Innovative Solutions for Overcoming Challenges
Successful incubators are employing innovative solutions to overcome funding limitations, attract high-quality mentors, and maintain program quality. For example, some incubators have established a tiered mentorship program, providing different levels of support based on mentor experience and availability. Others have developed robust fundraising strategies that combine venture capital, grants, and crowdfunding. Innovative approaches to program delivery, such as online learning platforms and virtual networking events, are also proving effective in addressing evolving needs and accessibility.
Impact on Entrepreneurship

Incubators are more than just physical spaces; they are vital catalysts for fostering a vibrant entrepreneurial ecosystem. They nurture not only individual ventures but also a broader culture of innovation and risk-taking. Their impact extends far beyond the startups they house, influencing the entrepreneurial spirit of entire communities and shaping the landscape of local economies.By providing resources, mentorship, and networking opportunities, incubators equip entrepreneurs with the tools and support needed to succeed.
This fosters a sense of collective entrepreneurial spirit, inspiring others to pursue their own ventures. Crucially, incubators play a pivotal role in supporting diverse founders, creating a more inclusive and equitable environment for all.
Fostering a Culture of Entrepreneurship
Incubators cultivate an environment where entrepreneurship thrives. They provide a dedicated space for aspiring entrepreneurs to connect, learn, and grow. This concentrated environment promotes knowledge sharing and collaboration, fostering a culture of innovation and support. Workshops, seminars, and networking events are frequently organized, facilitating the exchange of ideas and best practices amongst founders. This collaborative atmosphere encourages experimentation and risk-taking, crucial elements in entrepreneurial success.
Supporting Diverse Founders
Incubators are increasingly recognizing the importance of supporting women, minority, and underrepresented founders. Recognizing that diverse perspectives and backgrounds contribute significantly to innovation, incubators actively seek to create inclusive programs that address the unique challenges faced by these founders. This includes offering tailored mentorship, access to capital, and resources specifically designed to support their needs. Programs may include workshops on navigating gender bias in fundraising, or providing legal support for minority founders, creating a more equitable playing field.
Influencing the Entrepreneurial Spirit
Incubators aren’t just about individual startups; they inspire a wider community. The success stories emerging from incubator programs often ignite a desire to pursue entrepreneurial ventures in the surrounding community. The visible evidence of successful ventures within the incubator space creates a powerful demonstration of what is possible. The success of a local startup that began within an incubator often sparks the entrepreneurial spirit of others, generating a ripple effect throughout the community.
Impact on the Local Economy
Incubators significantly impact the local economy by creating jobs and attracting investment. Startups nurtured within incubator programs often expand rapidly, leading to the creation of new employment opportunities. The presence of successful incubators can also attract venture capital and angel investors to the region, stimulating further economic growth. This influx of investment capital further fuels innovation and job creation, leading to a virtuous cycle of economic prosperity.
Case Studies: Demonstrating Impact
Numerous case studies highlight the transformative impact of incubators on local economies. For instance, [Insert a hypothetical case study of an incubator in a specific region, detailing the number of startups created, jobs generated, and investment attracted]. This example illustrates the substantial contribution incubators can make to local economic development. Another example is [Insert another hypothetical case study of an incubator, highlighting the specific support given to diverse founders and the positive impact on the local community].
These examples showcase the multifaceted impact of incubators, not just on the individual startups, but also on the wider entrepreneurial ecosystem and the surrounding community.
Epilogue: E Incubators Paving The Way For Startups
In conclusion, e incubators are more than just spaces; they are catalysts for innovation and economic growth. Their ability to foster a supportive environment, connect startups with resources, and cultivate a culture of entrepreneurship is undeniable. While challenges like funding and attracting top mentors persist, the potential for e-incubators to continue shaping the startup landscape is enormous. The future looks bright for startups leveraging these valuable resources, as they continue to adapt to the evolving needs of entrepreneurs.