As e commerce flourishes taxman becomes impatient – As e-commerce flourishes, taxman becomes impatient, a growing concern for businesses and consumers alike. The rapid expansion of online shopping has outpaced traditional tax collection methods, leaving a gap that needs addressing. This is a complex issue with implications for everything from small businesses to global trade. How can tax authorities keep up with the innovation and scale of e-commerce, while ensuring fair and efficient tax collection?
This article explores the challenges and opportunities surrounding e-commerce taxation. We’ll delve into the specifics of current growth metrics, the diverse business models involved, and the varied tax implications. Furthermore, we’ll examine the strategies employed by tax authorities, the impact on businesses and consumers, and the potential future trends and solutions.
E-commerce Growth and Tax Implications

The rapid rise of e-commerce has fundamentally reshaped the retail landscape. From niche online boutiques to global behemoths, businesses are leveraging digital platforms to connect with customers worldwide. This growth, however, brings with it a complex web of tax implications that businesses must navigate to ensure compliance and profitability.The current state of e-commerce is characterized by substantial growth in sales figures, widespread user adoption, and increasing market share.
Global e-commerce sales are projected to reach astronomical figures in the coming years, challenging traditional brick-and-mortar retailers to adapt or face obsolescence. This surge is fueled by advancements in technology, including secure payment systems, reliable logistics, and user-friendly interfaces. Consumers now expect a seamless online shopping experience, further driving the growth of e-commerce.
E-commerce Sales Figures and Market Share
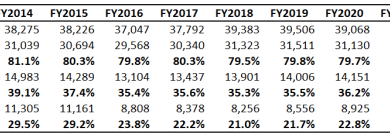
E-commerce sales have experienced exponential growth in recent years. Numerous reports from market research firms consistently demonstrate this upward trend, with projections suggesting continued robust growth. The market share held by e-commerce platforms continues to increase, impacting traditional retail models. This shift necessitates a proactive approach to understanding and addressing the evolving tax landscape surrounding e-commerce.
Historical Trends and Impact on Traditional Retail
The historical trend of e-commerce growth has been significant, with the early days characterized by a gradual increase in online sales, gradually transitioning to a rapid surge. The impact on traditional retail has been profound, forcing many brick-and-mortar stores to either adapt by incorporating online sales channels or risk decline. Successful adaptation often requires a holistic approach, incorporating digital strategies and innovative technologies.
Business Models and Tax Implications
E-commerce encompasses various business models, each with unique tax implications. Direct-to-consumer models, where businesses sell directly to customers, have different tax obligations compared to marketplace models. Dropshipping, where businesses act as intermediaries, requires careful consideration of tax liabilities at each stage of the transaction. Each model presents specific challenges and opportunities for tax compliance.
As e-commerce booms, tax authorities are understandably getting increasingly frustrated. The sheer scale of online transactions is proving tough to track and tax fairly. This pressure is clearly evident in the recent actions of Amazon, who’ve moved to head off potential legal challenges from the New York Times, potentially signaling a broader struggle to comply with evolving tax regulations.
Ultimately, this whole situation highlights the ongoing challenges of fairly taxing digital commerce in a rapidly changing world.
Types of Taxes Applicable to E-commerce Businesses
Several types of taxes affect e-commerce businesses. Sales tax is a significant consideration, particularly for businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions. Income tax obligations vary depending on the business structure and revenue generated. Value-added tax (VAT) is relevant for businesses operating in regions with VAT systems in place. Navigating these various tax obligations is crucial for e-commerce success.
Challenges Faced by E-commerce Businesses in Adhering to Tax Regulations
E-commerce businesses face significant challenges in adhering to tax regulations. Determining the correct jurisdiction for tax purposes, especially in cross-border transactions, can be complex. Keeping track of sales data across multiple platforms and jurisdictions is a demanding task. Staying updated with evolving tax laws and regulations requires ongoing effort. Furthermore, understanding the unique tax implications for different business models, such as dropshipping or subscription boxes, adds another layer of complexity.
Cross-Border E-commerce Transactions and Tax Collection
Cross-border e-commerce transactions introduce a significant layer of complexity in tax collection. Businesses need to understand the tax regulations of both the customer’s and the seller’s jurisdiction. This involves identifying the applicable sales tax rates, VAT regulations, and potential import duties. The increasing prevalence of cross-border e-commerce requires a nuanced understanding of international tax laws and compliance procedures.
Comparison of Tax Obligations for Different E-commerce Business Models
| Business Model | Sales Tax | Income Tax | VAT | Other Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct-to-Consumer | Collect sales tax in jurisdictions where the business has a physical presence or nexus. | Standard corporate income tax obligations. | Comply with VAT regulations in applicable jurisdictions. | Direct responsibility for fulfillment and customer service. |
| Marketplace | Often collect sales tax based on policies set by the platform. | Income tax on platform profits. | Comply with VAT regulations in applicable jurisdictions. | Less direct responsibility for fulfillment and customer service, but still subject to tax liability for the items sold. |
| Dropshipping | Potential tax liability in multiple jurisdictions based on customer location. | Income tax on profits. | Comply with VAT regulations in applicable jurisdictions. | Limited direct control over fulfillment and customer service. |
This table provides a concise overview of the potential tax obligations for various e-commerce business models. Further research into specific jurisdictions and business structures is essential for accurate tax planning.
Taxman’s Response to E-commerce Growth
The burgeoning e-commerce sector presents a unique challenge to tax authorities worldwide. As online marketplaces and global delivery networks proliferate, traditional tax collection methods struggle to keep pace with the rapid evolution of digital commerce. This necessitates innovative approaches to monitoring transactions, identifying potential tax evasion, and ensuring fair taxation across jurisdictions.The tax authorities are increasingly recognizing the need for proactive measures to address the complexities of e-commerce.
This includes leveraging technology, international cooperation, and adapting existing regulations to better encompass the unique characteristics of digital transactions. This dynamic landscape requires a constant adjustment to ensure that businesses and individuals comply with tax obligations, while also ensuring a fair and equitable system for all.
Current Strategies for Monitoring and Collecting Taxes
Tax authorities are employing various strategies to monitor and collect taxes from e-commerce businesses. These include enhanced data analysis, partnerships with businesses, and international collaborations. Understanding the strategies employed by various countries provides insight into the effectiveness and adaptability of different approaches.
Increasing Scrutiny of E-commerce Businesses
E-commerce businesses face increased scrutiny from tax authorities globally. This is driven by the desire to prevent tax evasion, ensure fair competition, and maintain a level playing field for all businesses. The complexity of cross-border transactions and the anonymity inherent in digital transactions makes identifying and tracking e-commerce activity a significant challenge for tax authorities. This is further exacerbated by the rapid pace of technological advancement, with new e-commerce models emerging constantly.
Methods for Tracking E-commerce Transactions
Tax authorities utilize a variety of methods to track e-commerce transactions and identify potential tax evasion. These include analyzing transaction data, cross-referencing information from various sources, and utilizing advanced data analytics tools. By correlating transaction details with business registration data, tax authorities can pinpoint discrepancies and anomalies, enabling them to take appropriate actions to ensure compliance.
Successful Tax Collection Strategies
Several countries have successfully implemented strategies for collecting taxes from e-commerce businesses. Examples include the use of data-driven approaches to identify and assess tax liabilities, the establishment of dedicated e-commerce tax units, and collaborations with international counterparts. For instance, some countries have introduced specific regulations for online marketplaces, requiring them to collect and remit sales taxes on behalf of sellers.
Challenges in Keeping Up with E-commerce Innovation
Tax authorities face significant challenges in keeping up with the rapid pace of e-commerce innovation. New technologies, such as cryptocurrencies and decentralized marketplaces, continuously emerge, requiring adaptation of existing regulations and monitoring techniques. The constant evolution of e-commerce models necessitates the development of novel strategies for tax collection and enforcement.
Comparison of Tax Collection Approaches
Tax collection approaches vary across countries and regions. Factors like the level of e-commerce development, existing tax infrastructure, and legal frameworks influence the methods employed. Some countries may have comprehensive digital tax regulations, while others may be adopting a more cautious approach. This difference in approaches necessitates international cooperation and the sharing of best practices to ensure a consistent and fair tax system.
Tax Rates and Regulations Across Jurisdictions
| Jurisdiction | Sales Tax Rate (e-commerce) | Tax Reporting Requirements | Compliance Penalties |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Vary by state, generally 4-10% | Detailed reporting of sales transactions | Significant fines for non-compliance |
| European Union | VAT rates vary by member state | VAT registration and reporting obligations | Penalties for non-compliance, including fines and potential criminal charges |
| China | Value-added tax (VAT) and business tax | Detailed transaction data reporting | Strict enforcement and penalties for non-compliance |
| India | GST (Goods and Services Tax) | Registration and reporting obligations | Penalties for non-compliance, including fines and legal action |
This table provides a simplified overview. Specific regulations and rates may vary based on the nature of the goods or services sold and the seller’s location. It is essential to consult the relevant tax authorities for the most up-to-date and precise information.
Impact on Businesses and Consumers: As E Commerce Flourishes Taxman Becomes Impatient
The burgeoning e-commerce sector faces a growing challenge: the increasing scrutiny of tax authorities. This heightened attention impacts both businesses and consumers, demanding adaptation and potentially altering the landscape of online retail. Businesses must navigate complex tax regulations, while consumers may face price adjustments and altered purchasing behaviors. Understanding these implications is crucial for anyone involved in or affected by the e-commerce industry.The tightening of tax regulations on e-commerce businesses introduces a significant operational cost.
Businesses must invest in compliance systems, including accounting software, legal expertise, and personnel dedicated to tracking and managing taxes across various jurisdictions. This investment directly translates into higher operational costs, potentially affecting profitability and pricing strategies. The burden of compliance, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), can be substantial.
Implications for E-commerce Businesses
The increased tax scrutiny on e-commerce businesses demands significant adjustments in their operational strategies. Businesses need to establish robust tax accounting procedures, accurately report sales, and comply with international tax regulations. This often requires substantial investment in specialized software and trained personnel to manage cross-border transactions and meet diverse tax requirements. For instance, businesses selling products internationally must adhere to the tax laws of each country where they operate, potentially leading to complex logistical and administrative hurdles.
Compliance Burden for E-commerce Businesses
E-commerce businesses face a substantial compliance burden. This involves accurate tracking of sales across various jurisdictions, ensuring adherence to local tax laws, and potentially managing different tax rates and filing requirements. For example, a business selling to customers in multiple EU member states would need to understand and comply with each country’s VAT regulations. The administrative costs associated with this compliance can be substantial, particularly for businesses with limited resources or those operating in multiple countries.
Furthermore, the risk of penalties for non-compliance can be significant.
Consequences for Consumers
Increased tax scrutiny on e-commerce businesses can translate into increased costs for consumers. Businesses may pass on the additional compliance and tax costs to customers through price increases, leading to potentially higher prices for goods and services. This impact is especially noticeable in markets with complex or evolving tax regulations. In addition to price increases, consumers might experience longer delivery times due to the complexity of international tax regulations, leading to higher transaction costs.
Comparison of Consumer Experiences
Consumers in countries with robust e-commerce tax systems generally experience a more transparent and predictable online shopping environment. They are often better informed about the tax implications of their purchases, and tax collection procedures are generally more efficient. In contrast, consumers in countries with less stringent e-commerce tax systems may encounter higher transaction costs, unclear pricing structures, or hidden taxes, leading to a less transparent and potentially less favorable shopping experience.
With e-commerce booming, tax authorities are understandably getting more vigilant. Navigating the complexities of online sales requires careful planning, and one crucial step is establishing a merchant account for your web business. This helps streamline transactions and accurately track income for tax purposes, ensuring you’re compliant while your e-commerce venture thrives. Properly setting up your online payments and accounting systems is key to maintaining a healthy relationship with the taxman as e-commerce continues its rapid growth.
establishing a merchant account for your web business
Examples of Tax Regulations Affecting Consumer Choices
Tax regulations can influence consumer choices when purchasing online. For instance, the introduction of a sales tax in a specific country might lead consumers to favor e-commerce businesses operating in regions with lower or no sales tax. Consumers may also opt for goods from businesses that explicitly disclose all taxes and associated costs upfront. Import duties and VATs can significantly influence the final price of goods, leading to conscious consumer choices regarding origin and price.
Implications for Small Businesses
Small businesses operating in the e-commerce sector face a unique set of challenges in complying with evolving tax regulations. Navigating diverse tax requirements across different jurisdictions and managing the associated administrative burden can be especially difficult for resource-constrained SMEs. Limited budgets may hinder their ability to invest in compliance software or hire specialized personnel, placing them at a disadvantage compared to larger enterprises.
The potential for penalties for non-compliance can also be a significant threat to the survival and growth of these businesses.
Impact of Tax Policies on Pricing, As e commerce flourishes taxman becomes impatient
| Tax Policy | Potential Impact on Pricing |
|---|---|
| Increased VAT rates | Higher prices for goods and services |
| Clearer cross-border tax rules | More transparent pricing, potentially reducing transaction costs |
| Simplified e-commerce tax filing requirements | Lower administrative costs, potentially leading to lower prices |
| Reduced import duties | Lower prices for imported goods |
Future Trends and Potential Solutions

The rapid growth of e-commerce presents both exciting opportunities and complex tax challenges. As online marketplaces expand globally, governments face the crucial task of adapting their tax systems to ensure fair and efficient revenue collection. This involves not only understanding the evolving nature of digital transactions but also anticipating future trends and developing innovative solutions to effectively manage e-commerce taxation.The projected surge in e-commerce activity will undoubtedly strain existing tax collection mechanisms.
As e-commerce booms, tax authorities are understandably getting increasingly impatient with the complexities of online sales. This is where innovative solutions like those offered by IBM and Novell come into play, with their new suite of e-commerce solutions aiming to streamline the process for both businesses and tax departments alike. IBM and Novell team up to deliver e-commerce solutions to help manage the growing digital marketplace, potentially alleviating some of the pressure on taxmen and improving the accuracy of tax collection.
Hopefully, these advancements will keep pace with the ever-expanding e-commerce sector and maintain a balance between its growth and effective taxation.
The sheer volume of transactions, the diverse range of products sold, and the global reach of online businesses make traditional tax methods less effective. This necessitates a proactive approach to tax administration that incorporates technological advancements and adapts to the ever-changing landscape of the e-commerce sector.
Projected Growth and Associated Tax Challenges
E-commerce is projected to experience exponential growth in the coming years. This expansion will be driven by factors like increasing internet penetration, mobile phone usage, and the rising popularity of online shopping. This growth, while beneficial for consumers and businesses, creates significant challenges for tax authorities. The decentralized nature of e-commerce transactions, coupled with the anonymity of many online platforms, can make it difficult to identify and track taxable activities.
Potential Solutions to Address Tax Collection Issues
Effective tax collection in the e-commerce sector requires a multifaceted approach. Key strategies include implementing robust data analytics tools, collaborating with e-commerce platforms, and streamlining international tax agreements. This will improve the identification of taxable transactions, enhance the transparency of online businesses, and ensure fair and equitable taxation for all participants in the e-commerce ecosystem.
- Data Analytics and Tax Administration: Sophisticated data analytics can play a vital role in identifying and tracking taxable transactions. By leveraging big data and machine learning algorithms, tax authorities can gain a deeper understanding of e-commerce activities, enabling them to improve tax collection efficiency. For example, analyzing transaction patterns and customer demographics can help identify potential tax evasion. Real-time data analysis can enable authorities to quickly detect and address suspicious activities.
- Enhanced Cooperation with E-commerce Platforms: Collaborating with e-commerce platforms can provide valuable insights into transaction data and facilitate tax compliance. Platforms can provide access to transaction details, enabling authorities to verify the tax obligations of businesses operating on their sites. This collaboration requires trust and clear guidelines to ensure data privacy and security.
- Streamlining International Tax Agreements: International tax agreements are essential for managing cross-border e-commerce transactions. Clear rules and regulations for taxation on international sales and the exchange of information between tax authorities are crucial to prevent tax evasion and ensure fair competition. This can be achieved through harmonization of tax laws and the development of effective dispute resolution mechanisms.
Technological Advancements and Their Impact
Technological advancements have significantly impacted the e-commerce landscape, and these same innovations offer solutions to enhance tax collection. Blockchain technology, for instance, can create a secure and transparent record of transactions, aiding in the verification of tax obligations. Cryptocurrencies, while posing challenges, also present opportunities for tracking transactions and implementing new tax policies.
Innovative Approaches to Tax Compliance
Innovative approaches to tax compliance for e-commerce businesses can foster a culture of transparency and accountability. This includes the use of automated tax calculation tools, which can help businesses accurately calculate and remit taxes. Additionally, offering tax education and support programs can empower businesses to understand and comply with tax regulations.
Evolving Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape surrounding e-commerce taxation is constantly evolving. Governments are actively seeking to adapt their tax laws to address the unique challenges of digital transactions. This includes updating existing laws to accommodate new technologies and creating new regulations tailored to the e-commerce sector.
Collaborations Between Businesses and Tax Authorities
Effective collaboration between e-commerce businesses and tax authorities is vital for achieving seamless tax collection. Open communication channels and joint initiatives can help establish clear guidelines, promote transparency, and create a conducive environment for compliance.
Potential Solutions Summary
| Solution Area | Potential Solutions |
|---|---|
| Data Analytics | Implement sophisticated data analytics tools, leverage big data and machine learning, and utilize real-time data analysis. |
| Platform Collaboration | Establish clear guidelines for data sharing and access, provide support and resources to e-commerce platforms for tax compliance. |
| International Agreements | Harmonize tax laws across borders, establish effective dispute resolution mechanisms, and facilitate the exchange of information between tax authorities. |
| Technological Advancements | Utilize blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies, and other innovative solutions for enhanced transparency and traceability. |
| Regulatory Landscape | Continuously update tax laws to accommodate new technologies, create new regulations tailored to the e-commerce sector, and promote transparency and accountability. |
| Business-Authority Collaboration | Establish open communication channels, implement joint initiatives, and promote compliance through education and support. |
Illustrative Cases
Navigating the complex landscape of e-commerce taxation requires understanding both the challenges and successful strategies employed by businesses. This section explores specific cases to illustrate the nuances of compliance and the consequences of non-compliance, offering valuable insights for both established and emerging e-commerce players.
Examples of E-commerce Businesses Facing Tax Challenges
E-commerce businesses often face unique tax challenges due to their dispersed operations and global reach. One common issue is determining the appropriate jurisdiction for tax obligations. For instance, a company selling products across multiple states in the US may struggle to calculate and remit sales taxes in each state where they have customers. Another challenge involves the complexities of international taxation, including VAT (Value Added Tax) and other local levies in different countries.
Small businesses, especially those operating in nascent markets, may lack the resources and expertise to navigate these complexities, leading to unintentional non-compliance. Furthermore, fluctuating market conditions and rapid growth can strain a business’s capacity to manage its tax obligations efficiently.
Cases of Tax Authority Action Against Non-Compliant Businesses
Tax authorities worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing e-commerce businesses for tax compliance. Instances of audits, penalties, and legal actions against businesses for failing to remit sales taxes, file required reports, or misrepresent their income are becoming more prevalent. These actions often stem from concerns about the potential for tax evasion and revenue loss. For example, a company operating a cross-border marketplace may be penalized for failing to collect and remit VAT in all the countries where they facilitate sales.
The scale of penalties can be substantial, impacting a business’s financial stability and reputation.
Examples of Successful E-commerce Businesses Managing Tax Obligations
Several e-commerce businesses have successfully managed their tax obligations, demonstrating that compliance is achievable with proactive strategies. These businesses often employ specialized tax advisors and utilize sophisticated accounting software to track sales, expenses, and tax liabilities across different jurisdictions. They proactively seek expert advice, often through professional accounting and legal firms, to ensure their practices align with the evolving regulations.
For example, Amazon, while facing numerous tax challenges over the years, has implemented systems to collect and remit sales taxes in various countries and established tax departments with significant expertise.
Case Study: The UK’s Approach to E-Commerce Taxation
The UK, like many other countries, has implemented measures to address the challenges of e-commerce taxation. A key aspect of the UK’s approach is its focus on digital services taxation (DST), aiming to capture revenue from businesses operating in the digital sphere. They’ve introduced specific rules for online retailers, often requiring them to register for VAT and pay taxes based on the location of their customers.
This approach aims to ensure a fair distribution of tax obligations. In addition, the UK utilizes data analysis to identify potential non-compliance issues.
Comparative Analysis of E-Commerce Tax Policies
Comparing e-commerce tax policies across different countries reveals significant variations. Some countries adopt a broad-based approach, encompassing all digital transactions, while others focus on specific sectors or types of e-commerce activities. Different countries use varying thresholds for tax obligations, which can impact small businesses. The complexities and inconsistencies in global tax policies present significant challenges for businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions.
Steps Taken by Businesses to Comply with Tax Laws
Businesses often implement various strategies to comply with tax laws in different jurisdictions. These steps include registering for relevant tax IDs in all applicable jurisdictions, accurately tracking sales and expenses related to each jurisdiction, and consulting with tax professionals to ensure compliance. Moreover, some companies utilize technology to automate tax reporting and compliance procedures. This helps to ensure the business operates within the legal framework.
Key Takeaways from E-Commerce Tax Cases
| Case | Issue | Outcome | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | Failure to remit sales taxes in multiple states | Penalties and legal action | Proactive compliance is crucial. |
| Company B | Misrepresentation of income | Audit and significant fines | Accurate record-keeping is essential. |
| Company C | Navigating international VAT | Successful compliance through expert advice | Professional guidance is valuable. |
Last Point
In conclusion, the rise of e-commerce presents a significant challenge to traditional tax systems. As e-commerce continues its rapid growth, tax authorities need to adapt their strategies to keep pace. This requires innovation, collaboration, and a willingness to embrace technological advancements. The implications for businesses, consumers, and the global economy are substantial, and careful consideration of these issues is crucial for a sustainable and equitable future.