Are you sick of the Microsoft antitrust case? This in-depth look delves into the public’s sentiment, historical context, economic impacts, legal arguments, potential outcomes, industry responses, alternative perspectives, and illustrative examples. We’ll examine the various angles of this complex legal battle, exploring its significance for the tech industry and consumers.
From public concerns about market dominance to the legal precedents being set, this exploration aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the case’s multifaceted nature. We’ll analyze the potential consequences for both Microsoft and the broader tech landscape.
Public Perception of the Microsoft Antitrust Case
The Microsoft antitrust case, a saga spanning decades, has consistently sparked public interest and debate. The ongoing scrutiny into Microsoft’s practices and its potential impact on the tech industry and consumers continues to generate discussion, often with differing viewpoints. Public perception is shaped by a complex interplay of factors, including perceived market dominance, innovation concerns, and the potential for consumer harm.
This analysis delves into the public’s concerns and perspectives surrounding the case.The public’s perspective on the Microsoft antitrust case is multifaceted. From accusations of anti-competitive behavior to concerns about the potential for stifling innovation, the case has ignited a broad range of reactions. The narrative surrounding the case is not always straightforward, with arguments presented from both sides, including Microsoft’s defense of its practices and the concerns raised by competitors and regulators.
Understanding the nuances of these perspectives is key to grasping the broader public sentiment.
Public Concerns Regarding the Case
The public’s anxieties about the case are largely rooted in concerns about the potential for reduced competition and innovation. Public discourse often highlights the fear of Microsoft leveraging its market dominance to unfairly disadvantage competitors and stifle emerging technologies. These concerns often manifest as worries about higher prices, reduced choice for consumers, and diminished innovation in the broader tech landscape.
- Market Dominance: A recurring concern revolves around Microsoft’s substantial market share in various software and services. The fear is that this dominance could translate into anti-competitive practices, limiting choices for consumers and hindering the growth of smaller companies. For instance, the concern that Microsoft’s operating system could become a barrier to entry for new players is a recurring theme in public discussions.
- Innovation Suppression: Another key concern is that Microsoft’s current and potential future actions could stifle innovation. The fear is that the company might prioritize maintaining its existing dominance over promoting groundbreaking advancements that could benefit the entire tech sector. This is often tied to concerns about the company’s influence over the development of essential technologies.
- Consumer Harm: Public anxieties often center on the potential for harm to consumers. This includes fears of higher prices, reduced product choices, and less competitive services. A common example of this is the concern that Microsoft might use its market power to limit access to essential software for consumers, effectively locking them into their ecosystem.
Potential Consequences for the Tech Industry and Consumers, Are you sick of the microsoft antitrust case
The outcome of the case has the potential to significantly reshape the tech industry. Depending on the court’s decision, it could either reinforce existing industry structures or pave the way for a more competitive landscape. The consequences for consumers could range from a continued reliance on Microsoft products to a wider variety of choices and potentially lower prices.
| Concern | Source | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Market Dominance | News Articles, Social Media | High |
| Innovation Suppression | Tech Blogs, Analyst Reports | Medium |
| Consumer Harm (Higher Prices, Reduced Choice) | Consumer Forums, Online Reviews | High |
“The potential for stifling innovation is a major concern for the tech industry, as it could discourage investment in research and development, leading to a stagnation of technological advancement.”
Historical Context of Antitrust Cases
The Microsoft antitrust case is far from unique. A rich history of similar battles over market dominance and innovation has shaped antitrust law and continues to influence the tech landscape today. Understanding this history helps contextualize the current case and offers valuable insights into the evolution of legal arguments and outcomes.The ongoing Microsoft case echoes past struggles with powerful tech companies, highlighting the delicate balance between fostering competition and allowing innovation.
The past provides crucial precedents for analyzing the present and predicting future developments. This exploration will delve into the historical context of antitrust law, tracing its evolution and examining relevant precedents in the tech industry.
Historical Overview of Antitrust Laws
Antitrust laws, designed to prevent monopolies and promote competition, have a long and evolving history. Their roots trace back to the late 19th century with the Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890, which aimed to curb the power of large corporations. Subsequent legislation, like the Clayton Act of 1914 and the Federal Trade Commission Act, further refined and expanded these principles.
These laws, and their subsequent interpretations, have been consistently refined over the decades to address new economic realities and evolving market structures.
Similar Antitrust Cases in the Tech Industry
Several tech companies have faced antitrust scrutiny throughout history. The cases often center around accusations of leveraging market dominance to stifle competition. One notable example is the AT&T case, where the company’s near-monopoly over telephone services led to significant legal challenges. Similarly, the Standard Oil case, a landmark antitrust case from the early 20th century, demonstrated the lengths to which the government will go to prevent monopolies.
Comparison of Legal Arguments and Outcomes
The legal arguments in previous tech antitrust cases often revolved around similar themes, such as tying arrangements, exclusive dealing agreements, and predatory pricing. However, the specific details and the legal interpretations of these practices have evolved over time. The outcomes of these cases have also varied, with some leading to substantial settlements and divestitures while others resulted in less stringent remedies.
Table: Comparison of Past and Current Antitrust Cases
| Case | Company | Charges | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT&T (1982) | American Telephone & Telegraph | Monopoly in telephone services | Forced divestiture of its local operating companies |
| Standard Oil (1911) | Standard Oil | Monopoly in oil refining and distribution | Forced breakup of the company into smaller entities |
| Microsoft (2000) | Microsoft | Abuse of monopoly power in operating systems market | Settlement including licensing requirements |
This table illustrates some key similarities and differences across various antitrust cases, highlighting the evolving nature of legal challenges and the complexities of enforcing antitrust laws in dynamic markets.
Economic Impacts of the Case
The Microsoft antitrust case, a protracted legal battle, is poised to have significant reverberations throughout the tech industry. Its outcome will not only shape the future of Microsoft but also influence the competitive landscape of software, gaming, and operating systems. Understanding the potential economic impacts is crucial for anticipating the winners and losers in this complex technological arena.The case’s impact extends beyond legal proceedings.
Honestly, are you sick of the Microsoft antitrust case? It’s been dragging on forever, hasn’t it? Meanwhile, look at this: Disney and Infoseek launched Go.com with 8 million users! disney and infoseek launch go com with 8 million users It’s a stark reminder of the vibrant online landscape emerging, and perhaps a little perspective on the long-drawn-out legal battles.
Still, I can’t help but wonder if the tech giants were more focused on innovation instead of legal battles, where would we be now? Are you still sick of the Microsoft antitrust case?
It will undoubtedly reshape market dynamics, potentially leading to shifts in consumer choices and business strategies. The economic effects are expected to be far-reaching, impacting not just Microsoft but also its competitors and the broader tech ecosystem.
Potential Winners
The antitrust case could create opportunities for competitors in the tech sector. If Microsoft’s dominance in certain areas is challenged, smaller companies and newer entrants could gain a larger market share. This could lead to increased innovation and competition, potentially benefiting consumers with more choices and better products. The case’s resolution could accelerate innovation in operating systems, and encourage advancements in alternative software.
This could be particularly impactful in the software sector if competitors are given a clearer path to market penetration.
Potential Losers
Conversely, the outcome of the case could negatively affect Microsoft’s market position. Potential losses in market share and revenue could occur, depending on the court’s decision. Specific sectors like gaming, where Microsoft has been actively expanding, could also be affected. If the case results in significant restrictions on Microsoft’s practices, its ability to innovate and expand in certain sectors could be curtailed.
Market Dynamics Affected
The antitrust case is significantly impacting the market dynamics of several key sectors. The software market will be influenced by the rulings on anti-competitive practices. The gaming market will experience changes based on Microsoft’s ability to integrate its gaming services. Operating systems are also affected as the case explores the limits of dominance in this crucial sector.
These changes will reverberate through the entire tech industry, creating a ripple effect that will impact various sectors.
Predicted Economic Impacts
| Sector | Potential Positive Impacts | Potential Negative Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Software | Increased competition, potentially leading to better products and lower prices for consumers. New opportunities for smaller software companies. | Reduced revenue for Microsoft, potentially impacting employment. Reduced innovation if Microsoft’s market dominance is curtailed. |
| Gaming | Expansion of gaming choices for consumers, greater competition in the gaming market. | Reduced potential for Microsoft to expand its gaming ecosystem if its practices are restricted. |
| Operating Systems | Greater choice for consumers, potentially driving innovation in alternative operating systems. | Loss of market share for Microsoft, potential reduction in revenue. |
The table above provides a preliminary overview of potential economic impacts. These predictions are based on current market trends and legal precedents, and the actual outcomes may vary.
Legal Arguments and Proceedings
The Microsoft antitrust case, a landmark battle in the tech world, revolved around complex legal arguments and proceedings. The case highlighted the tension between innovation and market dominance, prompting scrutiny of powerful companies’ practices. Understanding the legal maneuvers is crucial to grasping the lasting impact of this case on the tech industry and antitrust enforcement.The legal proceedings in the Microsoft case were characterized by intricate legal arguments presented by both sides.
These arguments explored the breadth and depth of antitrust laws, ultimately shaping how courts approach such disputes. The core issues centered on whether Microsoft’s actions constituted anti-competitive behavior, and if so, what remedies were appropriate.
Honestly, are you sick of the Microsoft antitrust case yet? It’s been dragging on for what feels like an eternity. Meanwhile, eBay is taking a proactive step forward by launching innovative shipping services, like the industry’s first online auction shipping services with mail boxes and integration with iShip.com ebay plans industrys first online auction shipping services with mail boxes etc and iship com.
Maybe this new focus on logistics will finally shift the conversation away from the endless legal battles and back to the real issues facing online commerce. Still, are you sick of the Microsoft antitrust case yet? I sure am.
Key Legal Arguments by Plaintiffs
The plaintiffs, primarily the U.S. Department of Justice and various state attorneys general, argued that Microsoft’s practices violated antitrust laws by leveraging its Windows operating system dominance to stifle competition. Their primary arguments focused on the following:
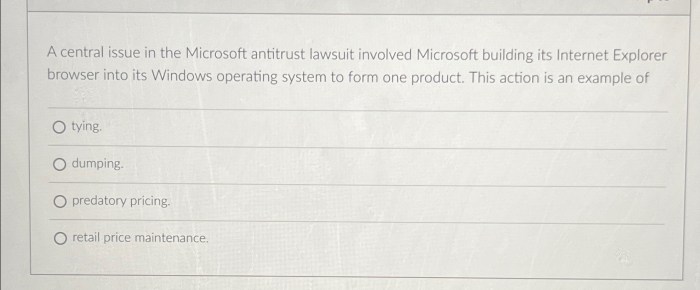
- Bundling of Internet Explorer: Plaintiffs contended that Microsoft’s practice of bundling Internet Explorer with Windows was anti-competitive, creating a barrier to entry for rival browser providers. They argued that this bundled offering gave Microsoft an unfair advantage, stifling innovation and competition in the browser market.
- Exclusive Dealing Arrangements: Plaintiffs also cited specific contractual arrangements Microsoft had with various companies, suggesting exclusive dealing arrangements that prevented competitors from gaining market share. They asserted that these arrangements limited consumers’ choice and stifled innovation.
- Predatory Pricing: The plaintiffs alleged that Microsoft engaged in predatory pricing strategies in the browser market. They argued that Microsoft set prices below cost for Internet Explorer to drive competitors out of the market, thus creating a monopoly and limiting consumer choice.
Key Legal Arguments by the Defendant
Microsoft countered these allegations, arguing that its actions were justified and did not constitute anti-competitive behavior. Their primary arguments revolved around:
- Innovation and Consumer Choice: Microsoft maintained that its bundling strategies were beneficial for consumers, offering a seamless integrated experience. They emphasized the value of choice in the marketplace and argued that consumers benefited from having a standard browser included in the Windows operating system.
- Interoperability and Compatibility: Microsoft highlighted the importance of interoperability and compatibility across different software and hardware. They asserted that their bundled software was necessary for maintaining a consistent and reliable platform.
- Competitive Advantages: Microsoft argued that its market dominance was a result of its innovation and superior products, not anti-competitive practices. They maintained that their market share reflected consumer preferences and technological superiority.
Relevant Legal Precedents
The Microsoft case drew upon several established antitrust precedents. These included cases like United States v. AT&T and United States v. IBM, which had set important legal precedents for evaluating anti-competitive practices and market dominance. These cases emphasized the need for a balanced approach that considered innovation and consumer welfare alongside the preservation of competition.
Honestly, I’m starting to feel a bit burnt out on the Microsoft antitrust case. It’s been dragging on, and frankly, I’m more interested in seeing how Toys ‘R’ Us is navigating the competitive waters of e-commerce. Their recent foray into the deep end of the e-commerce pool, as detailed in this article on toys r us dives into deep end of e commerce pool , is definitely a fascinating case study.
But let’s be honest, maybe the Microsoft case will finally wrap up soon, and we can all move on to something else.
Key Legal Issues and Implications
The Microsoft case highlighted several key legal issues with significant implications for the tech industry:
- Defining Market Power: The case emphasized the challenge of defining market power and assessing its impact on competition. The court needed to determine the boundaries of Microsoft’s market influence and its effect on rival businesses.
- Assessing Anti-Competitive Behavior: The case brought to light the intricacies of evaluating anti-competitive behavior in a rapidly evolving technological landscape. The court had to determine whether Microsoft’s actions constituted a violation of antitrust laws in the context of the dynamic software industry.
- Balancing Innovation and Competition: The case highlighted the delicate balance between encouraging innovation and protecting competition in dynamic industries. The court had to weigh the potential benefits of innovation against the need to prevent the abuse of market power.
| Plaintiff | Argument |
|---|---|
| U.S. Department of Justice | Bundling of Internet Explorer, exclusive dealing arrangements, predatory pricing |
| State Attorneys General | Similar to DOJ arguments, emphasizing state consumer interests |
| Defendant (Microsoft) | Argument |
| Microsoft | Innovation, consumer choice, interoperability, competitive advantages |
Potential Outcomes and Implications

The Microsoft antitrust case, a landmark legal battle, hangs in the balance, poised to reshape the future of the tech industry. The outcome will reverberate far beyond the courtroom, influencing not only Microsoft’s position but also the broader landscape of competition and innovation. Predicting the precise outcome is difficult, but considering various scenarios provides valuable insight into the potential ramifications.The implications of the ruling will be profound.
A favorable judgment for the plaintiffs could lead to significant regulatory changes, potentially fostering a more competitive tech market. Conversely, a victory for Microsoft could solidify its dominant position and potentially discourage future antitrust challenges. Understanding these potential outcomes is crucial for comprehending the long-term impact on the tech industry and the broader economy.
Potential Judgments and Their Probabilities
The outcome of the case hinges on the interpretation of the evidence presented and the legal precedents applied. Several potential judgments are conceivable, ranging from a complete dismissal to a comprehensive restructuring of Microsoft’s business practices. Assessing the likelihood of each outcome requires careful consideration of the strengths and weaknesses of both sides.
Implications of Different Judgments
Different judgments will have significantly different implications for the tech industry and future antitrust cases. A ruling against Microsoft, for example, could lead to a more fragmented tech market, potentially fostering innovation by preventing the consolidation of power in a single entity. Conversely, a ruling in Microsoft’s favor might solidify its position as a dominant player, potentially impacting the competitiveness of smaller firms and the future of innovation.
Impact on Future Antitrust Cases
The Microsoft case will undoubtedly set a precedent for future antitrust cases. The court’s decision will define the boundaries of acceptable business practices and influence how similar disputes are handled in the future. A stringent interpretation of antitrust laws could discourage aggressive business strategies and promote fairer competition. Conversely, a more lenient approach could lead to greater corporate consolidation and potentially limit the scope of antitrust enforcement.
Table of Potential Outcomes
| Outcome | Probability | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Complete dismissal of the case. | Low | Reinforces Microsoft’s current dominance, potentially discourages future antitrust challenges. |
| Partial victory for the plaintiffs. | Medium | Microsoft faces some regulatory restrictions, fostering greater competition but not significantly altering its overall position. |
| Comprehensive restructuring of Microsoft’s business practices. | Low | Significant alteration of Microsoft’s business model, creating a more competitive market but potentially harming Microsoft’s long-term profitability. |
| Complete victory for the plaintiffs. | Low | Forced divestiture of assets or significant restrictions on Microsoft’s operations, leading to a more fragmented tech market, but potentially hindering innovation and growth. |
Industry Responses to the Case
The Microsoft antitrust case, a landmark event in the tech industry, sparked a flurry of responses from competitors and industry leaders. These reactions, ranging from cautious observation to outright criticism, offer a fascinating glimpse into the strategic considerations and anxieties within the tech sector. The case’s implications for the future of competition and innovation are undeniably significant, forcing companies to recalibrate their strategies and public statements.The case isn’t just about Microsoft; it’s a test of the entire ecosystem.
Other tech giants, particularly those perceived as potential competitors or beneficiaries from the outcomes, have carefully weighed the implications of the ongoing legal battle. This careful maneuvering and reaction, in turn, shapes the future landscape of the tech world.
Responses from Other Tech Companies
The reactions from other tech companies varied significantly. Some expressed concern about the potential precedent the case could set for future antitrust investigations. Others viewed it as a necessary corrective action to maintain a fair and competitive market. These diverse responses highlight the complex and multifaceted nature of the case.
- Concerns about Precedent: Several companies publicly expressed concern about the potential for the case to establish a precedent that could stifle innovation and growth in the tech industry. These concerns were often voiced in private meetings and formal statements. They worried that similar actions could be taken against them, hindering their ability to introduce new technologies or services.
- Defense of Competition: Some tech companies, particularly those perceived as competitors to Microsoft in specific markets, openly defended the need for robust competition and expressed support for the investigation. They highlighted the potential benefits of a level playing field for all companies, and stressed that maintaining competition was crucial for consumers. Statements by executives from these companies often framed the case as a defense of consumer interests.
- Neutral Observations: A number of tech companies opted for a more neutral stance, avoiding direct criticism or endorsement. These responses, while not offering explicit opinions, nonetheless indicated a careful assessment of the case’s potential impact on their own operations and market positioning. These observations usually followed with a statement of adherence to legal requirements and market guidelines.
Statements by Tech Executives
A significant portion of the public response came in the form of statements made by executives from various tech companies. These statements, both public and private, revealed the nuanced reactions to the case. The different viewpoints reflect the diverse interests and strategic considerations within the tech industry.
“We believe in a fair and competitive marketplace, and we are committed to ensuring that our business practices comply with all applicable laws.”
Statement by a prominent tech executive, avoiding explicit stances but hinting at compliance and support for a level playing field.
- Support for Competition: Several executives publicly stated their support for maintaining a competitive market. They highlighted the importance of competition for innovation and consumer benefit, framing the Microsoft case as an issue of market integrity.
- Concerns about the Case’s Implications: Other executives expressed concerns about the potential ramifications of the case on the tech industry as a whole. These concerns included potential limitations on innovation and the impact on consumer choices.
Industry Reactions in Different Viewpoints
The reactions varied widely across different segments of the industry, reflecting differing perspectives and strategic considerations.
“The Microsoft case is a critical test of the antitrust laws in the digital age. A ruling against Microsoft could have a chilling effect on innovation.”
Industry analyst expressing a concern about the case’s potential implications.
| Industry Segment | General Reaction | Potential Impact on Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Software Developers | Mixed; some concerned about precedent, others supportive of maintaining competition | Potential shifts in development strategies to mitigate antitrust concerns; increased focus on independent software development |
| Hardware Manufacturers | Mostly neutral; focused on maintaining their own market positions | Potential adjustments to hardware strategies, potentially including diversification or focusing on non-Microsoft compatible systems |
| Internet Service Providers | Mostly neutral; focused on maintaining neutral network access | Potential adjustments to network management policies, ensuring fair access for all services |
Alternative Perspectives on the Case: Are You Sick Of The Microsoft Antitrust Case
The Microsoft antitrust case, while often framed as a battle between innovation and market dominance, presents a multifaceted picture with alternative viewpoints. These perspectives often challenge the core arguments of the prosecution, offering nuanced interpretations of the facts and potential unintended consequences of the outcome. Examining these counterarguments reveals a more complex landscape of economic forces and competitive strategies.Different stakeholders, from software developers to consumers, hold varying opinions on the case’s impact.
Understanding these diverse perspectives provides a more complete picture of the situation, moving beyond the typical binary narrative.
Challenging the Antitrust Claims
The arguments against the antitrust claims often focus on the dynamic nature of the tech industry and the complexities of innovation. These counterarguments highlight the perceived benefits of Microsoft’s actions, arguing that their strategies fostered competition and ultimately benefited consumers.
- Network Effects and Interoperability: Microsoft’s business model, particularly regarding Windows, leveraged network effects. This means the more users adopted the platform, the more valuable it became. Critics of the antitrust case argue that forcing interoperability might have hindered the development of these network effects, potentially slowing innovation and benefiting competitors with less established ecosystems.
- Competitive Advantages as Innovation Drivers: The case’s critics argue that Microsoft’s significant market share, while a concern in some sectors, could also be a catalyst for innovation. They believe a dominant player might have more resources and incentives to invest in research and development, pushing technological boundaries.
- Evolution of the Software Landscape: The tech industry is constantly evolving. The case was brought at a specific time. Proponents of Microsoft argue that the landscape has since changed, and that the initial concerns may not be as relevant in the present-day environment.
Stakeholder Perspectives
Different stakeholders in the tech industry held varying views on the case. These perspectives highlight the potential for diverse outcomes.
| Stakeholder | Perspective | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Software Developers | Some developers benefited from Microsoft’s platform and its vast user base. | A dominant platform offers a large user pool for developers, driving application innovation and expansion. |
| Consumers | Concerns existed about potential lack of choice and innovation stifling. | A dominant platform might lead to fewer choices and limit innovation in software development. |
| Competitors | Saw the case as an opportunity to gain market share. | The case’s outcome could have significant implications for the competitive landscape, potentially allowing competitors to capture market share. |
Counterarguments and Examples
A critical component of alternative perspectives involves presenting counterarguments to the prevailing viewpoint. These arguments often challenge the assumptions and evidence supporting the initial accusations.
“The case oversimplified the complex dynamics of the tech industry and its rapid pace of change.”
For example, the prosecution’s arguments regarding Microsoft’s bundling practices might be challenged by demonstrating how such bundling actually stimulated innovation in complementary products. Similarly, the argument that Microsoft’s dominance stifled competition could be countered by demonstrating the subsequent emergence of successful competitors in the software market.
Illustrative Examples of the Case
The Microsoft antitrust case is a complex tapestry woven from various threads of argumentation. Understanding the specific examples that underpin these arguments is crucial to grasping the core issues at play. These examples, ranging from specific product features to broader market trends, illustrate how Microsoft’s actions impacted competition and innovation. The case offers valuable lessons about the balance between innovation and market dominance.
Bundling and Integration of Products
The case highlights the controversial practice of bundling software. Microsoft’s strategy of integrating its Windows operating system with its Internet Explorer browser is a key example. This integration, while potentially convenient for consumers, raised concerns about the potential for anti-competitive behavior. The argument was that this practice stifled competition in the browser market and created a virtual lock-in for users of Windows.
It limited consumers’ choices and potentially led to higher prices or less innovative alternatives.
- Windows bundled with Internet Explorer: This practice effectively tied the popularity of the browser to the market dominance of Windows. Users were compelled to use Internet Explorer, as an alternative would require a significant investment in learning a new browser.
- Microsoft Office suite and Windows integration: This created a similar effect, creating a barrier for users considering alternative office suites and software packages.
Predatory Pricing and Exclusionary Practices
Microsoft’s pricing strategies, in some cases, are cited as examples of predatory pricing. The strategy was to drive competitors out of the market by setting artificially low prices, potentially below cost, until the competitor’s ability to operate was compromised. This created a barrier to entry, further consolidating Microsoft’s market position. Furthermore, Microsoft’s actions were seen by some as exclusionary practices, designed to keep competitors from gaining market share or innovating.
- The aggressive pricing strategy for Windows operating system: While Microsoft argued for the benefit of a low price, critics claimed this strategy aimed to exclude competitors and eliminate potential innovation.
- Suppression of open-source alternatives: Microsoft’s resistance to the adoption of open-source alternatives to its products, and the use of its market power to prevent the widespread adoption of such alternatives, were seen by some as exclusionary practices.
Market Dominance and Innovation
The case also explores the relationship between market dominance and innovation. Critics argued that Microsoft’s substantial market share in the operating system market stifled innovation in the software industry. The implication was that a company with such a strong foothold might not have the same incentive to innovate or adapt to market changes as a smaller competitor.
- Slow pace of innovation in some software areas: Critics argued that the lack of significant innovation in certain areas, where competitors had been pushing boundaries, was a consequence of Microsoft’s market dominance.
Impact on Specific Products/Services
The case had direct implications for specific software products. The potential exclusion of Netscape Navigator, a popular web browser, from the Windows operating system is a significant example. This exclusionary practice potentially led to significant losses for Netscape, highlighting the potential negative impacts of the case on smaller competitors.
- Netscape Navigator: The potential exclusion of Netscape Navigator and other competitors, as a result of the bundling of Internet Explorer, significantly impacted Netscape’s market share and ability to compete.
- Development of open-source alternatives: While not a direct outcome of the case, the debate surrounding it encouraged the development of open-source alternatives to Microsoft products, such as Linux and open-source office suites.
Final Summary
In conclusion, the Microsoft antitrust case is a multifaceted issue with far-reaching implications. Public sentiment, historical context, economic factors, and legal arguments all play crucial roles in shaping the narrative. The potential outcomes and industry responses further highlight the significance of this case. While a definitive conclusion is still pending, this exploration offers a nuanced understanding of the ongoing legal battle and its impact on the future of the tech industry.