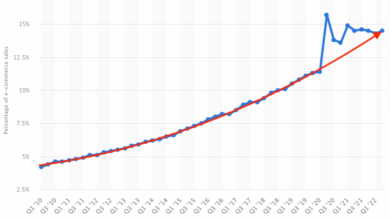
Internet taxes would cause drop in e commerce sales – Internet taxes would cause a drop in e-commerce sales, potentially impacting consumer behavior significantly. From budget-conscious shoppers to luxury buyers, everyone will likely adjust their strategies to avoid these new taxes. Will they opt for alternative payment methods, shop across borders, or return to physical stores? This deep dive explores the potential ramifications of internet taxes on the entire e-commerce ecosystem, from individual consumers to global trade relations.
This analysis examines how internet taxes could affect consumer behavior, impacting their purchasing decisions and potentially shifting spending habits. Different consumer groups will react in various ways, and this analysis Artikels how their responses might vary. The potential for price increases, reduced sales volumes, and altered business strategies for e-commerce companies will also be explored. The discussion will include a comparative look at how established companies and startups might be affected.
Finally, we’ll investigate the broader implications for the global e-commerce landscape, including cross-border transactions and potential trade disputes.
Impact on Consumer Behavior

The introduction of internet taxes could significantly reshape consumer behavior in the e-commerce landscape. Predicting the precise impact is complex, as consumer responses will vary based on individual circumstances and the specific tax structure implemented. However, several key trends are likely to emerge, affecting purchasing decisions and spending habits.
It’s a pretty common fear that internet taxes will significantly decrease e-commerce sales. People are worried that adding extra costs to online transactions could push customers away from digital shopping. This concern is especially relevant now, as companies like Applix, which recently set up an office for Linux development ( applix sets up office for linux ), are focused on the future of online services.
Ultimately, the impact of these taxes on online sales will be interesting to watch. Will these new policies make a dent in the booming e-commerce industry?
Consumer Reactions to Internet Taxes
The introduction of internet taxes will likely lead to a complex interplay of consumer responses. Budget-conscious consumers, prioritizing affordability, are likely to reduce their online spending, opting for physical stores or alternative online marketplaces without taxes. Value-seeking consumers, prioritizing the best deal, might be driven to compare prices across various online retailers and jurisdictions to find the lowest effective tax burden.
Luxury goods buyers, often less sensitive to price fluctuations, might still maintain online purchasing habits, as the tax burden might be absorbed into the higher price points.
Strategies to Avoid Internet Taxes
Consumers will likely employ various strategies to minimize the impact of internet taxes. One strategy involves seeking out alternative payment methods that may not be subject to the tax. This could include using payment services that operate outside the jurisdiction where the tax is levied. Another strategy might involve shopping in jurisdictions with lower or no internet taxes. Consumers could also adjust their spending habits, increasing purchases of physical goods, or seeking out local retailers that are not subject to the tax.
Shifting Consumer Spending Habits
The introduction of internet taxes might trigger a notable shift in consumer spending habits. Consumers may decide to increase their purchases of physical goods, as the price comparison with online retailers becomes less attractive due to the additional tax. Conversely, they might reduce or completely stop purchasing certain items if the price difference outweighs the value for them. The reliance on local retailers could also increase as a direct result of the tax, as consumers seek out tax-exempt options in their vicinity.
The overall impact on e-commerce and physical retail will depend on the specific tax structure and the consumer response.
Potential Reactions of Different Consumer Groups
| Consumer Group | Predicted Response | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Budget-conscious consumers | Reduce online spending, prioritize physical stores or tax-free online marketplaces. | Seeking the most affordable options and minimizing the tax burden. |
| Value-seeking consumers | Compare prices across online retailers and jurisdictions, potentially seeking the lowest effective tax burden. | Prioritizing the best value for their money and seeking the most favorable pricing structures. |
| Luxury goods buyers | May maintain online purchasing habits, as tax burden might be absorbed into higher price points. | Less sensitive to price fluctuations and potentially willing to pay the added tax. |
| Average consumers | Varying reactions depending on the specific tax structure and their spending habits. | A combination of factors including affordability, the need for the product, and the alternative options available. |
Economic Effects on E-commerce Businesses: Internet Taxes Would Cause Drop In E Commerce Sales
The introduction of internet taxes could significantly alter the landscape of e-commerce, impacting both established players and burgeoning startups. This shift stems from the need for businesses to adapt to the new financial framework, potentially leading to adjustments in pricing strategies, operational models, and overall profitability. The effect will be felt across the entire spectrum of e-commerce, from large corporations to smaller, independent online retailers.The potential consequences of internet taxes on e-commerce businesses are multifaceted.
Recent discussions about internet taxes have many worried about a potential drop in e-commerce sales. While the IRS deal boosting Beyond.com, as seen in this article, irs deal boosts beyond com , might seem positive, it doesn’t negate the broader concern. Increased taxes on online transactions could severely impact the industry, potentially driving consumers away from online shopping and towards brick-and-mortar stores.
These taxes will inevitably influence pricing models, impacting consumer behavior and ultimately affecting the revenue streams of e-commerce companies. Strategies for navigating this new economic reality will vary depending on the specific business model and the company’s existing financial standing.
Potential Consequences on Profitability
E-commerce companies will likely experience a direct reduction in profitability due to the added tax burden. This impact will be most pronounced for companies with higher sales volumes, as the tax burden will proportionally increase with the scale of operations. Reduced profitability could lead to a variety of responses, including price increases, reduced marketing budgets, or even strategic adjustments in business operations.
For example, companies might look to reduce their reliance on advertising, opting instead for more cost-effective methods of reaching consumers.
Price Increases and Sales Volumes
The imposition of internet taxes almost certainly leads to price increases for consumers. Companies will likely pass on the tax cost to customers, potentially leading to a decrease in sales volumes as consumers seek out more affordable alternatives. This is especially true for essential goods or products where price sensitivity is high. Historical examples of similar tax implementations on other sectors show a correlation between tax increases and reduced sales.
Impacts on Growth and Expansion Plans
The uncertainty surrounding internet taxes will undoubtedly affect the growth and expansion plans of e-commerce companies. Startups, particularly, may face significant challenges in securing funding and navigating the complexities of a new tax environment. Established companies, with their existing infrastructure and resources, may be better equipped to adapt, but even they may face obstacles in maintaining their current growth trajectories.
Adjusting Pricing Models
E-commerce companies will need to adapt their pricing models to account for the new tax burden. This may involve adjusting product pricing, introducing tiered pricing structures, or implementing subscription models to mitigate the impact of the tax. The specific adjustments will depend on the particular product or service offered.
Impact on Established vs. Startups
Established e-commerce companies, with their established customer bases and financial resources, are better positioned to absorb the impact of internet taxes. They have the flexibility to adjust pricing models and implement cost-saving measures to offset the tax burden. Startups, on the other hand, may struggle to absorb these costs and could face significant hurdles in maintaining profitability or even sustaining their operations.
Potential Revenue Impacts
| Business Model | Predicted Revenue Change | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Subscription-based services | Moderate decline | Higher fixed costs for tax compliance, potentially leading to price increases that could deter subscribers. |
| Marketplaces | Significant decline | Higher transaction costs could affect listing and purchasing activity, impacting overall revenue. |
| Direct-to-consumer sales | Significant decline | Price increases may lead to decreased sales, especially for essential goods or items with high price sensitivity. |
| Dropshipping | Moderate to high decline | Increased costs per order due to tax burden on each transaction, affecting profitability and potentially limiting expansion. |
Global E-commerce Landscape
The global e-commerce landscape is a complex tapestry woven from cross-border transactions, international regulations, and diverse business practices. The introduction of internet taxes, while potentially addressing revenue concerns in some nations, could significantly impact the intricate workings of this global marketplace. This section will delve into the implications of such taxes on the global e-commerce environment, exploring the potential for trade barriers and the varying approaches different countries might take.The imposition of internet taxes will inevitably reshape the global e-commerce landscape, particularly affecting cross-border transactions.
The current lack of standardized global regulations creates a challenging environment for businesses operating across multiple countries. This complexity will only intensify with the introduction of new taxes, forcing companies to navigate a patchwork of differing rules and compliance requirements.
Implications of Internet Taxes on Cross-Border Transactions
The introduction of internet taxes will significantly impact the ease and cost of cross-border e-commerce transactions. Businesses will need to factor in the tax liabilities in each jurisdiction where their customers reside. This could lead to higher prices for consumers, particularly for products from international sellers. This will likely result in consumers choosing cheaper domestic options, impacting international e-commerce sales.
Potential for Increased Trade Barriers
The introduction of internet taxes, especially if implemented inconsistently across borders, could create significant trade barriers. Businesses might face increased compliance costs, potentially leading to higher prices or reduced service offerings. This could discourage international expansion for many companies, impacting the flow of goods and services between countries. Moreover, the lack of clear and consistent tax rules could create uncertainty and hinder the development of a predictable global e-commerce ecosystem.
Comparison of Approaches to Implement Internet Taxes, Internet taxes would cause drop in e commerce sales
Different countries may adopt various approaches to implementing internet taxes, ranging from value-added taxes (VAT) models to digital services taxes (DST). Some countries might focus on taxing the revenue generated by online platforms, while others might opt for a destination-based system where taxes are levied based on the location of the consumer. These differing approaches will affect the global e-commerce ecosystem, impacting the competitive landscape and creating complex tax structures.
Examples of Existing Taxes on Digital Services
Several countries have already implemented digital services taxes, with varying impacts on e-commerce. For instance, the EU’s digital services tax has prompted discussions about its implications for cross-border businesses and consumer prices. Analyzing these existing examples is crucial in understanding the potential challenges and opportunities presented by the introduction of internet taxes on a broader scale.
Impact of International Regulations Surrounding Digital Taxation
International regulations surrounding digital taxation are crucial in mitigating potential trade disputes and ensuring a fair and predictable global e-commerce environment. These regulations will determine the extent to which countries can levy taxes on cross-border transactions and the impact on the competitiveness of different companies. A lack of harmonization could lead to significant challenges.
Potential Global Trade Disputes and Regulatory Challenges
| Country/Region | Potential Dispute | Possible Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| EU vs. USA | Disagreement on the appropriate taxation of digital services provided by US companies to EU consumers. | Negotiation of a mutual agreement on tax rules and jurisdiction. |
| Developing Countries vs. Developed Countries | Concerns that DSTs will disproportionately affect developing countries’ ability to compete in e-commerce. | Development of a global framework for digital taxation that considers the varying economic circumstances of different countries. |
| China vs. Other Countries | Disagreements on the taxation of digital platforms with significant operations in both China and other countries. | Bilateral agreements or international treaties to establish consistent tax rules. |
Alternatives and Mitigation Strategies
Navigating the potential pitfalls of internet taxation requires a multifaceted approach. Simply slapping a tax on internet activity risks stifling the vibrant e-commerce sector and potentially harming consumers. This section explores alternative revenue streams and strategies to lessen the negative impact of such taxes.A balanced approach is crucial. While governments need reliable revenue streams, they must also consider the economic realities of the digital marketplace.
Strategies that minimize disruption to e-commerce while ensuring sufficient tax collection are vital for sustainable growth.
Mitigation Strategies to Reduce Negative Impacts
Strategies to mitigate the negative effects of internet taxes on e-commerce sales require a combination of thoughtful policy design and adaptable business practices. Implementing these strategies can help maintain a healthy and competitive e-commerce landscape.
Internet taxes are a hot topic, and the fear is they’ll tank e-commerce sales. Think about it: older folks are increasingly comfortable online, and many are actually buying things while others just browse. Studies like surfing seniors buy while others browse show a definite buying power amongst this demographic. But if taxes are added, that could easily push them away from online purchases, causing a substantial drop in e-commerce sales.
- Targeted Taxation: Instead of a broad internet tax, governments can focus on specific digital services like digital advertising or data processing. This approach allows for a more nuanced approach to taxation, potentially generating revenue without disproportionately affecting e-commerce. For example, France levies taxes on digital advertising revenue, offering a model for selective taxation.
- Reduced VAT Rates or Exemptions: E-commerce businesses often face higher compliance costs and administrative burdens than traditional retailers. Offering reduced VAT rates or exemptions on specific e-commerce transactions can alleviate this burden. This would encourage the use of digital platforms and create a level playing field with traditional businesses.
- Streamlined Cross-Border Transactions: Simplifying cross-border e-commerce transactions, potentially through the use of digital platforms or tax treaties, can reduce the administrative burden on both businesses and consumers. This would encourage international trade and create a more efficient global marketplace. The European Union’s efforts to harmonize VAT rules across member states provide a framework for this type of approach.
- Investment in Infrastructure: Improvements in digital infrastructure, such as broadband access and data centers, can enhance the overall e-commerce experience. Increased investment in infrastructure will contribute to improved service delivery and promote e-commerce growth, offsetting potential tax burdens.
Alternative Revenue Streams
Alternative revenue streams beyond traditional internet taxes offer a more sustainable and equitable approach to generating government revenue in the digital economy.
- Taxation of Digital Advertising: Digital advertising is a significant component of the digital economy. Taxing this sector could generate substantial revenue without directly affecting e-commerce transactions. This model allows for a targeted approach to taxation while maintaining the vibrancy of the digital market. Many countries already tax advertising revenue in other sectors, so extending this to digital advertising is a logical progression.
- Taxation of Data Processing and Storage: Companies that process and store large amounts of data could be subject to specific taxes. This would help account for the significant value created by data in the digital economy. This approach would provide revenue from a sector that has experienced substantial growth in recent years.
- Adjusting Existing Taxes: Rather than creating new taxes, existing tax systems can be adjusted to better reflect the realities of the digital economy. For instance, sales taxes can be adapted to cover digital products and services, while adjusting tax rates for different types of e-commerce activities could also help generate revenue.
Designing Internet Taxes for Minimal Impact
The design of internet taxes is critical to minimizing their negative effects on e-commerce.
- Transparency and Predictability: Clear and transparent tax rules will help e-commerce businesses understand their obligations and plan accordingly. This approach reduces uncertainty and allows businesses to adapt to the new tax environment.
- Simplified Compliance: Implementing straightforward compliance mechanisms for e-commerce businesses will lessen the administrative burden. This approach would help to ensure the tax is levied fairly and efficiently.
- International Cooperation: International cooperation on digital taxation is essential to avoid double taxation and ensure a level playing field for e-commerce businesses operating across borders. International agreements and cooperation on digital taxation would ensure consistency and fairness in the global marketplace.
E-commerce Adaptation Strategies
E-commerce companies can adapt to a new tax environment through several strategies:
- Cost Adjustments: Businesses can adjust pricing strategies to account for the tax burden. This could involve adjusting product pricing or increasing shipping fees, thereby incorporating the tax into the overall cost.
- Operational Efficiency: Businesses can explore operational efficiencies to mitigate the impact of taxes. This may include optimizing supply chains, streamlining logistics, or reducing administrative costs.
- Tax-Efficient Structures: E-commerce companies can explore different business structures and legal frameworks to reduce their tax burden. This includes considering legal structures that are more tax-efficient in the new environment.
Historical Precedents and Analogies

The introduction of any new tax policy, especially one impacting a rapidly evolving sector like e-commerce, requires careful consideration of historical precedents. Understanding how similar policies have played out in the past can offer valuable insights into potential outcomes and inform the design of effective strategies to mitigate negative consequences. Examining historical tax policies, particularly those related to physical goods, can provide a crucial benchmark for evaluating the possible impact of internet taxes on consumer behavior and the e-commerce landscape.
Historical Examples of Similar Tax Policies
Various historical instances illustrate the complex interplay between taxation and economic activity. For example, the introduction of sales taxes in the 20th century often led to shifts in consumer purchasing patterns, with some products experiencing a decline in demand. The impact varied significantly depending on the specific tax rate, the type of product, and the overall economic climate.
Similarly, the implementation of value-added taxes (VATs) in numerous countries has profoundly affected pricing strategies and market competition. The impact on different industries, from manufacturing to retail, has been a mixed bag, demonstrating the nuanced nature of such policies.
Comparison of Internet Taxes with Other Forms of Taxation
Internet taxes differ significantly from traditional forms of taxation like sales taxes and VATs. While sales taxes typically apply to the final retail price of tangible goods, internet taxes are a newer concept and often lack a clear and uniform application. Sales taxes are relatively straightforward to administer in a brick-and-mortar setting, but the complexities of the digital marketplace make the application of internet taxes more challenging.
This difference in implementation and scope creates unique considerations for policy design and administration. Moreover, the digital nature of e-commerce transactions makes them less easily tracked compared to physical sales, raising potential challenges for revenue collection.
Impact of Taxes on Physical Goods Sales as a Benchmark
The impact of taxes on physical goods sales can serve as a useful benchmark for estimating the potential effects of internet taxes. For instance, increases in sales taxes on specific product categories often lead to consumers shifting their purchasing to tax-exempt or lower-taxed options. This substitution effect can be observed in both online and offline markets. Analyzing historical data on sales tax rates and consumer behavior in different regions can help anticipate potential trends for internet taxes, although the nature of the digital marketplace necessitates careful consideration of the unique dynamics of online sales.
Potential Parallels with the Evolution of Other Market Landscapes
The introduction of internet taxes presents potential parallels to the evolution of other market landscapes, such as the rise of the automobile industry. Early taxation policies related to automobiles, including licensing and fuel taxes, had significant implications for consumer behavior and the overall industry. Analyzing these historical examples can offer valuable insights into the possible adaptations and innovations that may emerge in the e-commerce sector in response to internet taxes.
Lessons from Historical Tax Policies
Historical tax policies, while not identical to the challenges posed by internet taxes, offer lessons regarding the importance of clear definitions, transparent application, and careful consideration of the economic impact. For instance, policies that promote clarity and predictability regarding the application of internet taxes can potentially minimize negative consequences. A well-designed policy framework, accounting for the specific characteristics of e-commerce, is essential to mitigate the potential negative impacts on both consumers and businesses.
Last Point
In conclusion, the introduction of internet taxes presents a complex challenge to the e-commerce industry. This analysis has explored the potential impact on consumer behavior, e-commerce businesses, and the global landscape. While the specific outcomes remain uncertain, the potential for a substantial drop in e-commerce sales, coupled with shifts in consumer behavior and business strategies, is a significant concern.
The analysis also highlights potential mitigation strategies and the importance of carefully considering the long-term implications of such taxation.