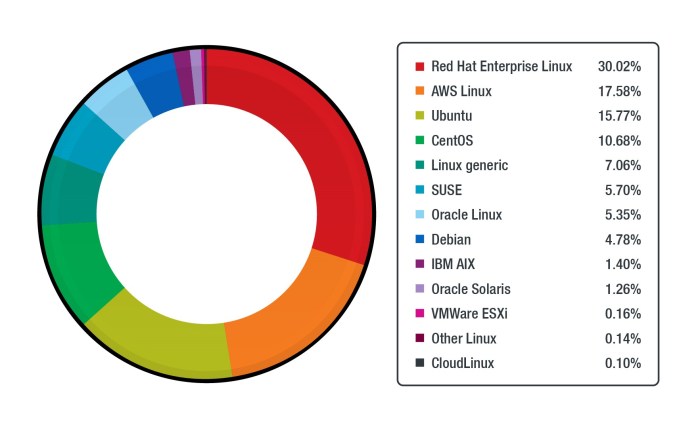
Will Linux skyrocket in developing countries? This question probes a fascinating intersection of technology and global development. The current landscape of Linux adoption in these regions reveals a complex mix of potential and challenges. From its cost-effectiveness to its open-source nature, Linux offers compelling advantages. However, hurdles such as a lack of skilled professionals and tailored software need careful consideration.
The existing infrastructure and support systems for Linux users in developing countries are a crucial element to consider. Examining specific sectors like education, healthcare, and government will provide valuable insight into the practical applications of Linux in these contexts. This analysis will delve into the potential of Linux to reduce reliance on expensive proprietary solutions and foster digital literacy in these communities.
Furthermore, the role of government policies and initiatives will be assessed, along with the availability of relevant hardware and software.
Linux Adoption in Developing Countries
Linux, a powerful and open-source operating system, has seen increasing interest in developing countries. Its cost-effectiveness, adaptability, and security make it an attractive alternative to proprietary solutions, particularly in regions with limited IT budgets and infrastructure. This article explores the current state of Linux adoption in these areas, focusing on its practical applications and the supporting ecosystem.
Current Presence in Developing Countries
Linux’s presence in developing countries is multifaceted. While not a dominant force like Windows or macOS, it has a strong foothold in specific sectors and is gaining traction in others. Its open-source nature enables customization and tailoring to local needs, making it a suitable choice for various applications. This flexibility is especially important in environments with diverse technical expertise and varying levels of infrastructure.
Key Sectors of Linux Use
Linux’s versatility is showcased in several key sectors. Government agencies, educational institutions, and non-profit organizations frequently utilize Linux servers for managing data and providing services. This is often due to the affordability and scalability of Linux-based solutions compared to commercial alternatives. Additionally, Linux is prevalent in the growing IT infrastructure of rural communities. The low cost of maintenance and the ability to customize systems to local needs makes it a valuable tool for supporting the growing digital landscape.
Infrastructure and Support Systems
The existing infrastructure and support systems for Linux users in developing countries vary widely. Some regions have robust online communities and user groups that provide assistance and guidance. However, other areas might lack the same level of readily available support. Local training programs and workshops are becoming increasingly important for bridging this gap. Efforts to cultivate local talent in Linux administration and development are vital to ensure the long-term sustainability of Linux-based projects.
Examples of Linux-Based Projects
Several compelling examples illustrate Linux’s role in development. Many educational institutions in Africa are deploying Linux-based computer labs to equip students with modern digital skills. Furthermore, non-profit organizations are utilizing Linux servers for managing their operations and delivering essential services to remote communities. These examples highlight the practical application of Linux in providing access to technology and fostering digital literacy.
Linux Adoption Rates Across Developing Countries
Unfortunately, precise, publicly available data on Linux adoption rates across developing countries is scarce. This makes a definitive table difficult to create. Gathering such statistics would require significant research and surveys tailored to specific regions and sectors.
| Country | Estimated Linux Adoption Rate (approximate, sector-specific) | Supporting Factors |
|---|---|---|
| India | High in specific sectors (e.g., open-source development, government) | Large IT talent pool, strong open-source community |
| Kenya | Growing in educational institutions, government services | Increased access to technology, digital literacy initiatives |
| Brazil | Moderate in government and research | Strong academic research community, national digital initiatives |
| Nigeria | Growing in specific sectors (e.g., small businesses, education) | Rising internet penetration, growing tech startup ecosystem |
The table above provides a generalized overview. The specific adoption rates in different sectors and regions within these countries may vary considerably. Further research and specific studies are needed to provide a more precise picture of the situation.
Factors Driving Potential Growth: Will Linux Skyrocket In Developing Countries
Linux’s potential for widespread adoption in developing countries hinges on its inherent advantages, particularly its cost-effectiveness and adaptability. The open-source nature of Linux reduces financial burdens compared to proprietary software, allowing governments and individuals to save substantial resources. This cost-effectiveness is crucial in regions where budgets are often stretched thin. Furthermore, the customization capabilities of Linux provide flexibility to tailor the operating system to specific needs and applications, further enhancing its value proposition.The significant role of open-source software in fostering digital inclusion in developing countries cannot be overstated.
By reducing dependence on expensive proprietary solutions, open-source platforms like Linux empower users and organizations with affordable access to powerful tools. This accessibility can stimulate innovation and create a more inclusive digital ecosystem, driving economic development and social progress.
Will Linux really take off in developing countries? It’s a compelling question, especially given the recent news about Compaq’s acquisition of Shopping.com, a significant move that could potentially reshape e-commerce. While the merger might seem unrelated, it hints at the growing digital landscape in these regions and the need for affordable, reliable operating systems. Ultimately, whether Linux gains widespread adoption in developing nations will depend on a variety of factors, including affordability, local support, and the availability of relevant applications.
Cost-Effectiveness and Customization, Will linux skyrocket in developing countries
Linux’s open-source nature significantly reduces licensing costs compared to proprietary operating systems. This translates to substantial savings for educational institutions, government agencies, and small businesses, allowing them to allocate resources to other crucial areas. Moreover, the modularity of Linux allows for customization to specific needs, such as tailoring the system to support particular hardware or software requirements common in developing countries.
This adaptability enhances its relevance and utility in various contexts.
Role of Open-Source Software
Open-source software, exemplified by Linux, plays a crucial role in reducing reliance on proprietary solutions. This reduction in reliance on expensive licensing fees allows organizations and individuals in developing countries to invest more in other critical areas, like infrastructure or training. The collaborative nature of open-source development empowers local communities to participate in the development and maintenance of software, fostering a sense of ownership and technical expertise.
This local involvement further enhances the sustainability and relevance of open-source solutions.
Linux in Education and Training
Linux’s affordability and accessibility make it an ideal platform for educational institutions in developing countries. By integrating Linux into curricula, educational institutions can provide students with valuable technical skills that are increasingly in demand in the global job market. Furthermore, Linux’s open-source nature encourages hands-on learning and problem-solving, enabling students to gain practical experience and contribute to the development of local communities.
Linux’s potential in developing countries is intriguing. The low cost and open-source nature of the OS could make it a game-changer for education and basic computing needs. However, the real-world implementation, and the need for a robust support system, often requires finding a qualified IT professional or a competent searching for a lawyer to navigate the legal landscape of software licensing and usage.
Ultimately, widespread Linux adoption hinges on factors beyond the operating system itself, and this makes predicting a skyrocket in popularity challenging.
Comparison with Other Operating Systems
While Windows and macOS are prevalent in many regions, Linux offers distinct advantages in the context of developing countries. The cost-effectiveness of Linux is a key differentiator, allowing educational institutions and businesses to allocate more resources to other critical aspects of development. The adaptability of Linux is another strength, allowing it to be tailored to specific needs and hardware, whereas other systems may not be as flexible.
Government Policies and Initiatives
Government policies and initiatives play a vital role in promoting Linux adoption. Encouraging the use of open-source software through incentives, training programs, and support for open-source communities can create a favorable environment for Linux adoption. By actively supporting Linux, governments can stimulate economic growth, enhance digital literacy, and foster a more robust and innovative technology sector within their countries.
Challenges and Obstacles
The path to widespread Linux adoption in developing countries is paved with significant hurdles. While the potential benefits are substantial, overcoming these obstacles will be crucial for realizing the positive impact of open-source software. These challenges range from a lack of technical expertise to limitations in hardware compatibility and software availability. Addressing these issues head-on is essential for fostering a robust and sustainable Linux ecosystem in these regions.The transition to Linux in developing nations faces considerable obstacles, not simply in terms of infrastructure but also in the availability of trained personnel and supportive environments.
These difficulties, if not adequately addressed, could significantly hinder the growth and sustainability of Linux adoption. A critical analysis of these obstacles is necessary to develop effective strategies for overcoming them.
Lack of Skilled Linux Professionals and Technical Support
The absence of a robust pool of skilled Linux professionals in developing countries presents a significant barrier to adoption. Finding individuals with the necessary expertise to install, configure, and maintain Linux systems is often challenging. This lack of technical support further complicates the process of troubleshooting issues and providing ongoing maintenance. Without trained personnel, the potential benefits of Linux, particularly in areas like education and small businesses, remain unrealized.
This scarcity of skilled labor is often exacerbated by the limited availability of training programs and educational resources specifically focused on Linux.
Hardware Compatibility and Software Availability Challenges
Linux’s success hinges on its compatibility with a wide range of hardware. In developing countries, the diversity of hardware often leads to compatibility issues. A lack of readily available drivers for local hardware can impede the smooth operation of Linux systems. Similarly, the availability of software tailored to the specific needs of these communities is crucial. The limited availability of software packages for tasks like accounting, local language support, or specific business applications hinders the practical application of Linux.
Availability of Tailored Linux Distributions
The landscape of Linux distributions isn’t uniform. While mainstream distributions like Ubuntu and Fedora exist, tailored distributions catering to specific needs in developing countries are often lacking. Distributions that are optimized for limited bandwidth, localized languages, and specific use cases (like educational software) are crucial for a smooth and efficient transition. The absence of such tailored solutions could lead to frustration and ultimately discourage broader adoption.
Consideration of local languages and cultural nuances is essential in creating distributions that resonate with the target users.
Obstacles to Training and Education
Effective training and education are paramount for widespread Linux adoption. Obstacles to these include a shortage of training facilities, limited access to educational resources, and a lack of experienced instructors. In addition, the cost of training materials and the time commitment required can be prohibitive for individuals and organizations in developing countries. The creation of accessible, affordable, and localized training programs tailored to specific skills and needs is critical.
A structured approach to education and practical application is essential to bridge the skills gap and empower communities to utilize Linux effectively.
Potential Applications and Use Cases
Linux’s open-source nature and flexibility make it a compelling choice for developing countries, offering numerous potential applications across various sectors. Its cost-effectiveness, scalability, and adaptability are particularly attractive in contexts where resources are often limited. This adaptability is crucial in tailoring solutions to the specific needs of diverse communities and supporting local development initiatives.The potential of Linux extends beyond simply being an operating system.
It empowers local communities and governments with tools and resources for fostering digital literacy, building robust infrastructure, and promoting economic growth. The availability of free and open-source software is key to leveraging Linux’s potential.
Government Applications
Linux’s robust infrastructure and security make it an ideal choice for government services. It can be used for various applications, from managing public records and delivering citizen services to running essential infrastructure systems.
Education Applications
Linux’s open-source nature and wide range of software make it an excellent platform for education. Its versatility allows for customized learning environments and the development of specialized educational software.
Healthcare Applications
Linux’s stability and reliability are beneficial for healthcare applications. It can be used for managing patient records, running diagnostic tools, and supporting telemedicine initiatives. This is particularly useful in regions with limited access to advanced technology.
Infrastructure Projects
Linux-based solutions are suitable for developing country infrastructure projects. For example, Linux can power the software behind smart grids, water management systems, and other essential utilities. This reduces costs associated with licensing proprietary software.
Digital Literacy Promotion
Linux’s open-source nature makes it accessible and easy to learn. This feature allows for the creation of educational resources and training programs to promote digital literacy, enabling individuals to utilize technology effectively. Linux distribution can be customized to meet the needs of specific educational environments.
While the potential for Linux to surge in developing countries is exciting, it’s worth considering the current internet access and shopping trends. Recent studies, like studies pinpoint future internet shoppers lagging areas , highlight areas where internet penetration and e-commerce adoption are still limited. This could significantly impact the growth of Linux-based systems if the underlying infrastructure isn’t robust enough to support it.
Ultimately, widespread Linux adoption in these regions hinges on broader internet accessibility and a thriving digital economy.
Small Businesses and Entrepreneurship
Linux’s cost-effectiveness and wide range of software options make it a suitable platform for small businesses and entrepreneurs in developing countries. This can support the growth of local businesses and foster innovation. This can enable small businesses to utilize essential software applications without incurring high licensing costs.
Improving Local Digital Infrastructure
Linux-based solutions can be employed to enhance local digital infrastructure. Open-source software can be tailored to meet specific needs and improve the efficiency of local networks. This is crucial for facilitating digital inclusion and connecting communities. For example, using Linux-based servers and networking tools can create more affordable and reliable internet access.
| Sector | Potential Applications |
|---|---|
| Government | Public record management, citizen services, infrastructure management |
| Education | Customizable learning environments, educational software development, online learning platforms |
| Healthcare | Patient record management, diagnostic tools, telemedicine support |
| Infrastructure | Smart grids, water management systems, essential utilities |
| Small Businesses | Accounting software, customer relationship management (CRM), e-commerce platforms |
Future Outlook and Projections
The future of Linux adoption in developing countries hinges on several factors, including the ongoing digital transformation, the increasing demand for affordable and reliable technology, and the potential for local partnerships to support the ecosystem. A robust and evolving Linux community can play a crucial role in bridging the digital divide and empowering these regions. While challenges remain, the potential for Linux to thrive in these contexts is significant.The trajectory of Linux adoption in developing countries will likely be characterized by a gradual yet steady increase, driven by the increasing availability of affordable hardware, the growing demand for open-source solutions, and the development of tailored Linux distributions.
Current trends suggest a growing preference for open-source software among developers and businesses in these regions, a preference that often translates to cost savings and improved sustainability.
Potential Future Scenarios
Several scenarios can be envisioned for the future of Linux in developing countries. One possibility involves Linux becoming a dominant operating system in certain sectors, such as government institutions and educational settings, leveraging its cost-effectiveness and security advantages. Another scenario envisions Linux gaining traction in specific industries, like mobile technology or cloud computing, adapting to local needs and fostering innovation.
Growth Trajectory Predictions
Based on current trends, Linux adoption in developing countries is projected to exhibit a gradual but steady growth pattern. Factors like the growing digital literacy, the availability of affordable internet access, and the development of localized support networks will contribute to this increase. This growth will likely vary across different countries, influenced by their unique economic conditions, technological infrastructure, and cultural contexts.
Role of International Collaborations
International collaborations and partnerships play a vital role in promoting Linux adoption in developing countries. These partnerships can provide technical support, training programs, and access to resources, accelerating the growth of local Linux communities and supporting the development of tailored solutions. For example, initiatives that pair experienced Linux developers in developed nations with aspiring developers in developing countries can foster knowledge transfer and expertise.
Projected Growth in Specific Countries
| Country | Projected Growth Rate (2024-2029) | Factors Influencing Growth |
|---|---|---|
| India | 15-20% | Large pool of skilled developers, government initiatives supporting open-source, increasing use in education |
| Nigeria | 10-15% | Growing internet penetration, demand for cost-effective solutions, emerging mobile technology sector |
| Kenya | 12-18% | Strong tech startup ecosystem, focus on digital literacy programs, growing demand for cloud services |
| Brazil | 10-15% | Large and established tech sector, government policies encouraging innovation, existing Linux infrastructure |
The table above provides illustrative projections, and actual growth rates may vary based on various local conditions.
Potential Impact on Local Economies
Linux’s widespread adoption in developing countries has the potential to significantly impact local economies. Open-source software, including Linux, often promotes cost savings for businesses and governments, leading to increased productivity and efficiency. The creation of local Linux communities and the development of specialized skills can also foster job creation and stimulate innovation within the tech sector. For instance, local businesses can leverage Linux for their operations, reducing their reliance on proprietary software and potentially lowering their costs.
Ending Remarks
Ultimately, the potential for Linux to transform digital landscapes in developing countries is undeniable. Its cost-effectiveness, open-source nature, and versatility present a strong argument for its widespread adoption. However, overcoming the existing challenges related to infrastructure, skills gaps, and software availability will be critical. The future trajectory of Linux adoption hinges on targeted support, tailored distributions, and strategic partnerships.
A nuanced understanding of the existing landscape, coupled with proactive strategies, will be essential to unlocking the full potential of Linux in these regions.