Financial services industry missing e commerce boat – Financial services industry missing e-commerce boat. The financial services industry has been slow to embrace e-commerce, lagging behind other sectors like retail and travel. This has created a gap in how consumers interact with financial institutions, leading to a disconnect between customer expectations and the services offered. The traditional model of brick-and-mortar branches and phone banking is increasingly being challenged by the rapid advancements and accessibility of e-commerce.
This article will delve into the reasons behind this lag, examining the historical context, the evolving e-commerce landscape, and potential strategies for catching up.
The historical context reveals a gradual shift in customer interaction methods. Early online banking initiatives struggled to match the convenience and speed of other sectors. Regulatory hurdles and security concerns also presented significant obstacles. This article will explore the unique challenges faced by financial institutions in adapting to the digital age, analyzing the specific barriers and examining potential solutions.
Historical Context of Financial Services
The financial services industry, a cornerstone of modern economies, has undergone a remarkable transformation. From its humble beginnings in the form of local bartering and credit systems, it has evolved into a complex global network facilitating countless transactions and influencing the course of global commerce. This evolution has been intricately tied to technological advancements and changing societal needs.This journey encompasses not only the rise of sophisticated financial instruments but also the shift in how customers interact with financial institutions.
This evolution is crucial to understanding the current landscape and anticipating future trends. The historical perspective reveals a dynamic relationship between innovation, customer experience, and the ever-evolving technological capabilities.
Early Stages and Brick-and-Mortar Dominance
Financial services in their nascent stages were largely localized and relied on personal relationships. Local merchants and lenders facilitated transactions, often through informal credit arrangements. The rise of formal financial institutions, marked by the establishment of banks and other financial intermediaries, brought about a shift towards standardized procedures and broader accessibility. Early banks primarily focused on safekeeping deposits and providing loans to businesses and individuals.
Physical branches became the primary interface between customers and financial institutions.
Evolution of Customer Interaction
The transition from traditional brick-and-mortar branches to online banking represents a significant paradigm shift in customer interaction. Early online banking solutions, while groundbreaking, faced challenges in terms of security and widespread adoption. Concerns about data security and the reliability of online transactions were prevalent, particularly in the initial years of online financial services.
Technological Adoption Compared to Other Industries
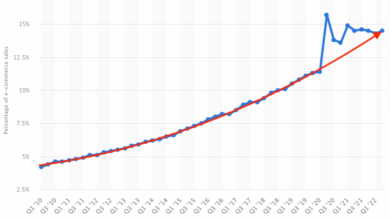
The financial services industry’s adoption of technology, while substantial, has lagged behind some other sectors, such as retail and e-commerce. While the industry has embraced automation in back-office operations and risk management, customer-facing interactions have sometimes been slower to adopt innovative technologies. This can be attributed to the stringent regulatory environment and the need for robust security protocols.
The need for high levels of security and compliance played a significant role in this slower adoption.
Early Online Transactions and Limitations
The early days of online financial transactions were characterized by a series of limitations. Security concerns, coupled with a lack of user-friendly interfaces, made online banking less appealing to the average consumer. Many individuals remained hesitant to embrace the new technology due to concerns about fraudulent activities and data breaches. The limited availability of reliable internet infrastructure and the digital literacy gap further contributed to the slow pace of adoption.
A critical element in overcoming these limitations was the development of secure payment systems and user-friendly interfaces.
Key Milestones in Financial Services Technology
- The introduction of automated teller machines (ATMs) in the 1960s revolutionized access to cash, enabling customers to perform transactions 24/7.
- The emergence of online banking in the 1990s opened new avenues for customer engagement and financial management, although security remained a significant concern.
- The proliferation of mobile banking applications in the 2000s and 2010s further enhanced convenience and accessibility, making financial services more integrated into daily life.
The evolution of these technologies highlights the ongoing quest to improve efficiency and enhance the customer experience in the financial services industry.
Comparing Adoption with Other Industries
| Industry | Adoption Speed | Factors Affecting Adoption |
|---|---|---|
| Retail | Relatively faster | Increased competition and consumer demand for convenience. |
| E-commerce | Very rapid | Ease of online transactions and global reach. |
| Financial Services | Moderate | Strict regulations, security concerns, and complex transactions. |
The table demonstrates a difference in adoption rates between industries. The financial sector’s slower pace reflects the higher risk and regulatory hurdles inherent in financial transactions. Factors such as the need for data security and compliance with financial regulations played a critical role in shaping the pace of technological advancements in this industry.
E-commerce Landscape and its Impact

The e-commerce revolution has fundamentally reshaped the way consumers interact with businesses across virtually every sector. From the convenience of browsing products at any time to the ease of comparing prices and services, the digital marketplace has altered consumer expectations. This rapid evolution has had profound implications for traditional industries, including financial services, forcing them to adapt or risk being left behind.The e-commerce sector has experienced explosive growth fueled by technological advancements and a rising demand for online convenience.
This growth has been facilitated by improvements in user experience, including intuitive interfaces, secure payment systems, and readily available customer support. Accessibility has also played a crucial role, with e-commerce platforms increasingly catering to diverse user needs, from mobile-first designs to support for various languages and payment methods. This has enabled broader participation and fostered a more inclusive digital marketplace.
Impact on Consumer Expectations and Demands
The proliferation of e-commerce has significantly altered consumer expectations across numerous industries. Consumers are now accustomed to instant gratification, personalized recommendations, and seamless online experiences. This heightened expectation for speed, convenience, and personalization has trickled down into all aspects of the consumer journey, including financial services. Consumers expect similar ease of use and convenience from their financial institutions as they experience in other online sectors.
Transformation of Customer Interaction and Expectations
E-commerce has fundamentally transformed customer interaction and expectations across various industries. The ability to access information, compare products, and make purchases at any time has empowered consumers. This newfound power has led to a shift in customer-vendor dynamics, demanding greater transparency, responsiveness, and personalized service. Financial institutions need to recognize and adapt to this evolving customer mindset to maintain competitiveness.
The financial services industry seems to be lagging behind in the e-commerce revolution. It’s a shame, really, considering how much potential there is for growth and innovation. Meanwhile, companies like Webtrends are stepping up their game by launching a new site specifically designed for internet professionals, demonstrating how important digital strategies are. This new site, webtrends unveils new site for internet professionals , could offer valuable insights for those in the financial services industry who are still struggling to catch up with the e-commerce curve.
For example, online banking and investment platforms have become indispensable for many, who expect instant account access, real-time transaction tracking, and personalized financial advice.
Comparison of E-commerce User Experience
| Feature | Financial Services | Retail | Travel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ease of Information Access | Online account statements, investment portfolio summaries, and real-time transaction details are crucial. Information should be easily accessible and understandable. | Product details, reviews, and comparisons are vital. Visuals, detailed descriptions, and user ratings are paramount. | Flight schedules, hotel availability, and travel options must be easily searchable. Visualizations of itineraries and price comparisons are critical. |
| Payment Options | Secure online payment platforms are essential for transferring funds and completing transactions. Multiple secure payment methods are crucial. | Diverse payment methods (credit/debit cards, online wallets) are needed to accommodate consumer preferences. Security is paramount. | Flexibility in payment methods is key. Online payment portals and secure transactions are required. |
| Customer Support | 24/7 online chat support, FAQs, and online help centers are necessary to address customer queries promptly. Accessibility to customer service is critical. | Responsive customer service through various channels (phone, email, chat) is expected. Quick resolution of issues is vital. | 24/7 online help, clear contact information, and prompt response to inquiries are expected. Customer service should be readily available. |
| Personalization | Tailored investment recommendations, personalized financial advice, and customized account settings are desired. Individual needs are crucial. | Product recommendations, tailored promotions, and personalized shopping experiences are expected. Customer data privacy is paramount. | Personalized travel recommendations based on past bookings and preferences are sought after. Customizable itineraries are desired. |
The table highlights the similarities and differences in the e-commerce user experience across various sectors. The level of personalization and ease of information access are key differentiators. Financial services are distinct in their need for robust security measures.
Financial Services’ E-commerce Lag
The financial services industry, historically slow to embrace e-commerce, faces unique challenges compared to other sectors. While online shopping and digital transactions are commonplace for many goods and services, the intricacies of finance, coupled with regulatory frameworks and security concerns, have created a distinct path for its digital transformation. This divergence has left many financial institutions struggling to keep pace with the rapid advancements in online platforms.The financial services industry’s adoption of e-commerce is often slower due to a complex interplay of factors.
The financial services industry seems to be perpetually missing the e-commerce boat, struggling to adapt to the digital age. While other sectors are rapidly embracing online platforms, this industry often lags behind. Interestingly, Corel’s recent Linux OEM agreement with PC chips, detailed in this article corel signs linux oem agreement with pc chips , highlights a different kind of digital transformation, one that could potentially offer new avenues for innovation and streamline processes.
Perhaps this shift, in a completely different sector, will inspire the financial industry to finally catch up and modernize its offerings.
These factors include the inherent complexity of financial products, the need for robust security measures, and the rigorous regulatory environment.
Key Reasons for Slower Adoption
The financial services industry, compared to other sectors, faces unique hurdles in embracing e-commerce. Regulatory compliance and security considerations play a significant role in the slower adoption of digital channels. These factors, along with the complex nature of financial products and services, contribute to the industry’s lag in fully utilizing e-commerce potential.
- Complexity of Financial Products: Financial products, including loans, investments, and insurance, are often complex and require detailed explanation and personalized advice. These characteristics make them less suitable for simple, standardized online interactions, unlike products sold directly to consumers.
- Regulatory Compliance and Security: Financial institutions are subject to stringent regulations regarding data protection, transaction security, and anti-money laundering (AML) measures. Meeting these compliance requirements can be resource-intensive and challenging to implement effectively within existing systems.
- Customer Trust and Perceived Risk: Consumers may be hesitant to conduct sensitive financial transactions online, fearing security breaches or fraudulent activities. Building trust and assuring consumers of secure online platforms is critical for the success of e-commerce in this sector.
Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance Issues
Financial institutions are bound by strict regulatory frameworks that differ significantly from other sectors. These regulations often impose specific requirements for data security, transaction verification, and reporting, creating significant challenges for e-commerce implementation.
- Data Security Regulations: Regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) mandate strict data handling procedures for personal financial information. These regulations necessitate significant investments in security infrastructure and compliance training to ensure data protection in online transactions.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) Compliance: AML and KYC regulations require financial institutions to verify the identities of customers and monitor transactions for suspicious activity. These processes are often more complex in the digital realm and require robust technological solutions to maintain compliance.
- Cross-Border Transactions: Financial transactions across borders often necessitate adhering to numerous international regulations, adding significant complexity to the process and potentially creating compliance challenges. Navigating these nuances is a considerable hurdle for financial institutions implementing e-commerce strategies on a global scale.
Security Concerns and Solutions
Security is paramount in online financial transactions. Addressing concerns related to data breaches and fraud is crucial for building consumer trust. Robust security measures are essential to mitigate risks.
- Enhanced Security Protocols: Financial institutions employ advanced encryption techniques, multi-factor authentication, and fraud detection systems to safeguard sensitive data. These protocols are continually refined to address evolving threats in the digital landscape.
- Data Encryption: End-to-end encryption and secure transmission protocols are employed to protect data during transit. The implementation and maintenance of such systems can be complex, requiring specialized knowledge and expertise.
- Security Infrastructure: Secure payment gateways, robust server infrastructure, and intrusion detection systems are crucial components of online financial transaction security. These components must be constantly monitored and updated to ensure resilience against emerging cyber threats.
Adapting Successful E-commerce Strategies
Examining successful e-commerce strategies in other industries provides valuable insights for the financial services sector. These strategies can be adapted and tailored to address the unique challenges and opportunities in finance.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Successful e-commerce models prioritize user experience. Financial institutions can adapt this principle by creating user-friendly platforms that simplify complex financial tasks and offer personalized support. This requires understanding customer needs and preferences.
- Personalized Financial Advice: E-commerce platforms often leverage algorithms to offer tailored recommendations. Financial institutions can adapt this by utilizing similar technologies to provide personalized financial advice and product suggestions.
- Transparency and Trust: Transparency in pricing, fees, and product information is essential. This creates trust with customers and encourages them to engage with financial institutions online.
Barriers to Entry and Adoption

Financial institutions, despite the undeniable push toward digital transformation, face unique challenges in their e-commerce journey. The transition from traditional brick-and-mortar operations to online platforms requires a significant shift in mindset and infrastructure. This shift isn’t just about building a website; it involves establishing trust, security, and a user-friendly experience for a highly sensitive market.
Technical Complexities of Secure Online Financial Platforms
Building robust e-commerce platforms for financial services necessitates a high degree of technical expertise and security measures. The need for secure data transmission, encryption, and fraud prevention is paramount. Integrating various systems, from customer relationship management (CRM) to payment gateways, requires meticulous planning and execution. Furthermore, ensuring the platform is compatible with diverse operating systems and browsers is crucial for a seamless user experience.
The complexity often involves integrating existing legacy systems with new e-commerce solutions, which adds another layer of technical challenge.
Cost Implications of E-commerce Infrastructure
Developing and maintaining e-commerce infrastructure for financial services involves significant capital expenditure. The costs extend beyond simply building a website; they encompass secure server infrastructure, robust cybersecurity measures, compliance with stringent regulations, and ongoing maintenance. Financial institutions must consider the expenses associated with staff training, software licenses, and regular updates to ensure the platform remains secure and compliant.
The substantial investment required often deters smaller institutions from pursuing e-commerce solutions.
Successful E-commerce Implementations in Financial Services
Several financial institutions have successfully transitioned to robust e-commerce platforms. Examples include banks that have integrated online banking services with mobile apps, offering 24/7 access to accounts and transactions. A key factor in their success is a deep understanding of customer needs and preferences. They prioritize intuitive interfaces and clear communication, focusing on a user-friendly experience. Another crucial aspect is focusing on secure and efficient payment processing, enabling customers to make transactions quickly and safely.
These successes underscore the potential of e-commerce when properly executed.
The financial services industry seems to have missed the boat on e-commerce, a glaring oversight. Companies like Akamai, however, are clearly capitalizing on the massive growth in online shopping. Their success in this space, as detailed in akamai riding the e commerce wave , highlights the industry’s potential for e-commerce integration, a crucial element that many financial institutions are still lagging behind on.
This lack of adaptation could put them at a significant disadvantage in the long run.
Overcoming Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
The financial services industry is heavily regulated. Implementing e-commerce solutions necessitates meticulous adherence to regulations like KYC (Know Your Customer), AML (Anti-Money Laundering), and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation). Financial institutions must ensure their e-commerce platforms comply with these regulations to avoid penalties and maintain customer trust. This often involves significant adjustments to existing internal processes and establishing robust compliance frameworks.
Navigating these hurdles requires expert legal counsel and ongoing monitoring to stay compliant with evolving regulations.
Emerging Trends and Future Prospects: Financial Services Industry Missing E Commerce Boat
The financial services industry is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements and evolving customer expectations. E-commerce adoption, while lagging behind other sectors, is poised for significant growth as innovative solutions emerge and barriers to entry diminish. Understanding these emerging trends is crucial for navigating the future of financial services and ensuring continued relevance in the digital age.The financial services industry is witnessing a fundamental shift towards digitalization, driven by a desire to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and provide more personalized customer experiences.
This digital transformation is impacting every aspect of the industry, from customer onboarding and account management to investment advice and fraud detection.
Emerging Technologies Reshaping the Industry
The financial services sector is being revolutionized by a plethora of innovative technologies. Mobile banking, for instance, has become ubiquitous, allowing customers to manage their finances anytime, anywhere. Fintech solutions, like peer-to-peer lending platforms and robo-advisors, are disrupting traditional financial institutions by offering more accessible and often more cost-effective services. These technologies are streamlining processes, improving accessibility, and enabling personalized financial solutions.
- Mobile Banking: Mobile banking apps have become integral to everyday financial transactions. They allow users to check balances, transfer funds, pay bills, and access financial advice through their smartphones, leading to increased convenience and accessibility. This trend is expected to continue, with even more sophisticated features and integrations into other applications.
- Fintech Solutions: Fintech companies are innovating in various areas, such as payments, lending, and investment management. Peer-to-peer lending platforms, for example, connect borrowers and lenders directly, often bypassing traditional banks and offering potentially lower interest rates. Robo-advisors automate investment strategies based on algorithms, providing cost-effective and accessible investment options for a wider range of individuals.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning are transforming customer service and fraud detection. Chatbots powered by AI can handle routine customer inquiries, freeing up human agents to deal with complex issues. Machine learning algorithms can identify fraudulent transactions with greater accuracy and speed, reducing financial losses.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning, Financial services industry missing e commerce boat
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are playing increasingly significant roles in enhancing customer experiences and service delivery. AI-powered chatbots can handle routine inquiries, providing immediate assistance and improving response times. ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential risks, thereby improving fraud detection and reducing financial losses. These technologies are enhancing efficiency and enabling more personalized services, making the financial industry more responsive and customer-centric.
Blockchain’s Potential for Enhanced Security and Transparency
Blockchain technology offers the potential to revolutionize online financial transactions by improving security and transparency. Its decentralized nature and cryptographic security measures can enhance the integrity of transactions and reduce the risk of fraud. This technology is still under development, but its potential to streamline processes and build trust in online financial interactions is significant. Early applications include cryptocurrencies and secure digital identity management.
Future Scenarios for E-commerce in Financial Services
The adoption of e-commerce in financial services is expected to vary significantly based on technological advancements and customer acceptance. The following table illustrates potential future scenarios:
| Scenario | Adoption Rate | Technological Advancements | Impact on Financial Services |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rapid Adoption | High | Advanced AI and ML, widespread blockchain adoption, seamless mobile integration | Disruption of traditional institutions, personalized financial services, increased accessibility |
| Moderate Adoption | Medium | Improved mobile banking, development of secure fintech solutions, enhanced AI-powered customer support | Evolution of existing institutions, emergence of new players, improved efficiency |
| Slow Adoption | Low | Limited integration of new technologies, resistance to digital transformation by some institutions | Continued dominance of traditional institutions, slower pace of innovation |
Customer Experience Analysis
The customer experience is paramount in any industry, and financial services e-commerce is no exception. A positive online experience fosters trust, encourages repeat business, and ultimately drives profitability. Understanding the factors that contribute to a positive customer experience in this sector is crucial for financial institutions to thrive in the digital age.
Factors Influencing Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction in financial services e-commerce hinges on several key factors. These include ease of navigation, clarity of information, security protocols, and responsiveness of customer support. A seamless and intuitive interface significantly impacts the user’s overall perception of the platform.
Importance of User-Friendliness, Security, and Trust
User-friendliness is critical for a positive customer experience. A well-designed platform should be intuitive and easy to navigate, minimizing the time and effort required to complete transactions. Security is paramount. Robust security measures, such as encryption and multi-factor authentication, build trust and assure customers that their sensitive financial data is protected. Trust is built over time and reinforced by transparent practices, clear communication, and consistent reliability.
Comparison of Customer Experiences Across Platforms
Different financial institutions employ varying approaches to e-commerce. Some platforms focus on simplicity and intuitive design, while others emphasize advanced features and functionalities. Comparing these platforms reveals a spectrum of customer experiences. For example, a bank offering basic online banking might excel in ease of use for routine transactions, whereas a brokerage platform might prioritize advanced charting tools and complex investment options, catering to sophisticated users.
Structured Analysis of Customer Feedback
A structured approach to analyzing customer feedback is essential for identifying areas for improvement. This approach involves gathering feedback through various channels, such as surveys, online reviews, and support tickets. Analysis should focus on specific aspects like usability, security, and accessibility. For example, analyzing customer feedback regarding the complexity of investment options can help tailor the platform to different user needs.
Furthermore, feedback on security concerns can help improve security measures and address customer anxieties.
Usability, Security, and Accessibility Analysis Framework
- Usability: Evaluate the ease of navigation, clarity of information, and efficiency of completing transactions. Assess the intuitiveness of the platform, the clarity of instructions, and the availability of helpful resources. For instance, consider the time required to complete a transaction, the number of steps involved, and the clarity of error messages.
- Security: Assess the effectiveness of security measures in place. Evaluate the use of encryption, multi-factor authentication, and data breach protection protocols. Identify any reported security concerns or vulnerabilities. For example, measure the speed of response to security incidents and the clarity of communication regarding security updates.
- Accessibility: Evaluate the platform’s accessibility for users with disabilities. Ensure compliance with accessibility standards, such as WCAG guidelines. Consider the availability of alternative text for images, keyboard navigation options, and adjustable font sizes. For example, test the platform with screen readers and other assistive technologies.
Customer Interaction Channels
Different customer interaction channels offer varying degrees of convenience and support. Understanding these channels allows institutions to tailor their approach to meet customer needs.
| Channel | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mobile App | Dedicated mobile banking application | Convenience, accessibility, real-time updates | Potential for security risks if not well-protected |
| Website | Online platform for transactions and information | Accessibility, wider reach, detailed information | Potentially less convenient for complex transactions |
| Phone Support | Human interaction for complex issues | Personalized assistance, problem resolution | Longer wait times, limited availability |
| Chat Support | Real-time support via text | Faster response, efficient communication | Limited ability to address complex issues |
Potential Strategies for Catching Up
The financial services industry has been slow to embrace the transformative potential of e-commerce. While online banking and mobile apps have become commonplace, a significant gap remains in fully leveraging the opportunities presented by digital platforms. This lag leaves financial institutions vulnerable to competition from nimble fintech companies who are rapidly adapting and exceeding customer expectations in the digital sphere.Catching up requires a multi-faceted approach that blends technological innovation with a deep understanding of customer needs and preferences.
This necessitates a shift from a traditional, branch-centric model to one that is customer-centric and digital-first. The key lies in creating seamless and intuitive online experiences that replicate the trust and security that customers expect from their financial institutions, while simultaneously improving operational efficiency.
Embracing Digital Transformation
Financial institutions must prioritize the development of user-friendly, secure, and intuitive online platforms. This involves designing responsive websites and mobile apps that cater to diverse customer needs and preferences, offering a consistent and positive user experience across all devices. Implementing robust security measures is paramount to maintain customer trust in a digital environment. Furthermore, integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) can significantly enhance customer service by providing personalized recommendations, proactive fraud detection, and automated customer support.
Creating Innovative Online Experiences
Creating an innovative online experience involves more than just a sleek website. It requires a profound understanding of customer behavior and preferences. Financial institutions should leverage data analytics to identify customer pain points and tailor their online offerings accordingly. For example, offering personalized financial advice and investment recommendations based on individual customer profiles, leveraging AI-powered chatbots to provide instant support, and developing interactive educational resources can significantly improve customer engagement.
The goal is to transform the often-daunting experience of financial transactions into an intuitive and positive one.
Partnering with Fintech Companies
Collaboration with fintech companies can accelerate the adoption of e-commerce strategies and provide valuable insights into emerging technologies and market trends. Fintech companies possess a unique understanding of digital platforms, customer engagement, and payment processing, enabling financial institutions to quickly integrate advanced e-commerce functionalities. This collaboration is not about replacing traditional services, but rather supplementing and augmenting them with cutting-edge digital capabilities.
Potential Partnerships and Benefits
- Partnership with a mobile payment platform: This can enable faster and more convenient transactions, potentially reducing reliance on physical branches and increasing customer satisfaction. The benefit is a more efficient and accessible payment system for customers.
- Collaboration with a robo-advisory platform: This partnership can provide access to sophisticated investment tools and personalized financial advice, potentially attracting younger generations of investors. The benefit is expanded financial service offerings with increased accessibility and customization.
- Alliance with a digital identity verification provider: This can strengthen security protocols and streamline the customer onboarding process, leading to a more secure and efficient online experience. The benefit is enhanced security and streamlined onboarding for customers.
- Partnership with a blockchain technology company: This could facilitate faster and more secure cross-border transactions, opening up new markets and enhancing global reach. The benefit is enhanced security, speed, and accessibility for international financial transactions.
Technological Enhancements for Operational Efficiency
Implementing technologies like cloud computing, automation, and API integrations can significantly reduce operational costs and improve efficiency. Cloud-based solutions can streamline back-office operations, while automation tools can reduce manual processes, freeing up staff to focus on higher-value tasks. API integrations can facilitate seamless data exchange between different systems, improving data accuracy and reducing errors. This will not only reduce costs but also enhance the overall customer experience.
Closure
In conclusion, the financial services industry’s reluctance to fully embrace e-commerce has created a noticeable gap compared to other sectors. This has impacted customer experience and overall service delivery. While regulatory hurdles and security concerns are valid considerations, the industry can learn from successful e-commerce strategies in other sectors. By adopting innovative technologies and partnering with fintech companies, financial institutions can bridge the gap and enhance customer satisfaction.
The future of financial services will undoubtedly rely on a seamless and user-friendly e-commerce experience, allowing consumers to access services with the same ease and convenience as other industries.