Security firm warns of new e commerce threat – Security firm warns of new e-commerce threat, highlighting a sophisticated and potentially damaging attack vector targeting online retailers. This new threat leverages vulnerabilities in e-commerce platforms, potentially impacting both businesses and consumers. The attack methods are detailed, exploring how attackers exploit weaknesses and the potential for significant financial and reputational damage.
The nature of the threat encompasses a range of technical aspects, including the type of malware employed, the attack vectors used, and the methods attackers use to exploit vulnerabilities. This analysis will delve into common vulnerabilities in e-commerce systems, outlining specific weaknesses in payment gateways, order processing, and APIs. Further, the impact on consumers and mitigation strategies will be examined, providing actionable advice for both businesses and individuals.
The Evolving Landscape of E-commerce Threats
The digital world is constantly evolving, and with it, the tactics of cybercriminals targeting e-commerce businesses. Recent advancements in attack techniques and vulnerabilities have led to a new threat, posing significant risks to businesses’ financial health and reputation. Understanding this threat is crucial for proactive security measures.
Nature of the New E-commerce Threat
This emerging threat leverages a sophisticated combination of techniques, targeting vulnerabilities in payment processing systems and customer data handling. It’s characterized by a novel approach that blends social engineering with automated attack tools. Attackers utilize phishing emails and malicious websites disguised as legitimate e-commerce platforms to capture login credentials and sensitive financial data.
Technical Aspects of the Attack
The attackers exploit vulnerabilities in web application frameworks and payment gateways by injecting malicious scripts. These scripts are designed to steal customer credit card information, login credentials, and other sensitive data during online transactions. Malicious code is often embedded in seemingly harmless website elements, making detection challenging. One key component is the use of polymorphic malware, which modifies its code structure to evade traditional security software.
Attackers frequently utilize botnets to overwhelm targeted systems, generating a high volume of fraudulent transactions.
Attack Methods and Exploitation
Attackers employ various methods to exploit vulnerabilities in e-commerce platforms. They often leverage phishing campaigns targeting employees and customers, tricking them into providing sensitive information. This tactic, combined with automated scripts, can quickly overwhelm security measures. Sophisticated techniques include credential stuffing, where stolen credentials from previous breaches are used to access accounts, and man-in-the-middle attacks that intercept and modify transactions.
Financial and Reputational Damage
The consequences of successful attacks can be devastating. Businesses face significant financial losses from fraudulent transactions, chargebacks, and the cost of incident response. Stolen customer data can lead to hefty fines under data privacy regulations and damage the company’s reputation, eroding customer trust and potentially leading to a decline in sales. In extreme cases, a breach can result in the complete loss of customer confidence and business closure.
Past E-commerce Attacks: Lessons Learned
Numerous e-commerce platforms have experienced attacks in the past, demonstrating the recurring nature of these threats. The 2017 Equifax breach, for example, highlighted the vulnerability of large datasets to sophisticated attacks, affecting millions of consumers. The similarities between past attacks and the current threat underscore the need for constant vigilance and robust security measures.
Comparison of Threats
| Threat Type | Attack Vector | Impact | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Previous Credit Card Skimming | Physical devices, compromised POS systems | Financial loss, data breaches | Moderate |
| Phishing Attacks | Emails, malicious websites | Data breaches, financial losses | High |
| New E-commerce Threat | Malicious scripts, polymorphic malware, botnets | Significant financial and reputational damage, substantial data breaches | Increasing |
Vulnerable E-commerce Systems
E-commerce platforms, while offering convenience, are increasingly vulnerable to sophisticated attacks. These vulnerabilities often stem from the complex interplay of interconnected systems, from payment gateways to order fulfillment, creating weak points that attackers can exploit. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for businesses to implement robust security measures and safeguard their operations and customer data.
Common Vulnerabilities in E-commerce Systems
E-commerce platforms face a range of vulnerabilities, from insecure APIs to outdated software. These vulnerabilities are often exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access, manipulate data, or disrupt services. Attackers target weak points in the platform’s architecture, often leveraging readily available exploits.
Weaknesses in Payment Gateways
Payment gateways are critical components of e-commerce systems, handling sensitive financial information. A major vulnerability lies in insecure communication protocols, which can expose transaction details to eavesdropping attacks. Insufficient encryption and weak authentication mechanisms further exacerbate the risk. Furthermore, outdated or poorly maintained payment gateways can be exploited by attackers to gain access to customer credit card numbers or other sensitive data.
Weaknesses in Order Processing Systems
Order processing systems, responsible for managing customer orders, are also susceptible to various vulnerabilities. Insecure input validation allows attackers to inject malicious code or manipulate order details, potentially leading to fraudulent orders or unauthorized changes. Poorly configured access controls can grant unauthorized users access to sensitive order information. The absence of regular security audits and updates exposes the system to known vulnerabilities.
Security Measures for E-commerce Platforms
Implementing robust security measures is essential for mitigating these vulnerabilities. These measures should address the diverse security needs of e-commerce platforms. Regular security audits, penetration testing, and vulnerability assessments can help identify and address weaknesses before they are exploited.
- Employ strong encryption protocols for all sensitive data transmissions.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all user accounts to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regularly update software and libraries to patch known vulnerabilities.
- Implement secure coding practices to prevent vulnerabilities in the platform’s codebase.
- Restrict access to sensitive data based on the principle of least privilege.
- Conduct regular penetration testing to identify and address potential weaknesses.
Leveraging Insecure APIs and Outdated Software
Attackers frequently exploit insecure APIs and outdated software. Insecure APIs often lack proper authentication and authorization mechanisms, allowing unauthorized access to sensitive data or functionality. Outdated software is vulnerable to known exploits, which attackers can readily leverage to gain control of the system.
Security Controls to Protect Against New Threats
Implementing specific security controls is crucial to protect against emerging threats. These controls must be tailored to the specific vulnerabilities and risks of the e-commerce platform.
| Vulnerability | Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Insecure API endpoints | Unauthorized access to sensitive data or functionality | Implement robust authentication and authorization mechanisms for all API endpoints. Utilize API keys and tokens for secure communication. |
| Outdated software | Exploitable vulnerabilities | Regularly update software and libraries to the latest versions. Establish a patching schedule and monitor for updates. |
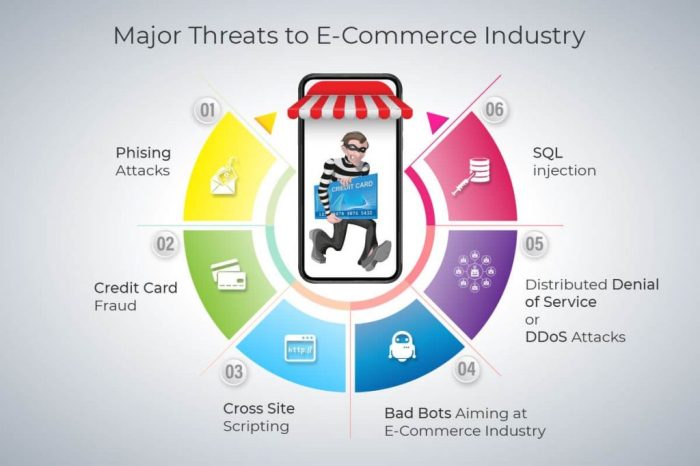
| SQL injection | Data breaches and manipulation | Validate all user inputs to prevent malicious code injection. Use parameterized queries to prevent SQL injection attacks. |
| Cross-site scripting (XSS) | Malicious scripts execution | Input validation to prevent script injection and output encoding to neutralize malicious scripts. |
| Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) | Unauthorized actions | Implement anti-CSRF tokens to verify the authenticity of requests. Use secure session management techniques. |
Customer Impact and Mitigation
The rise of sophisticated e-commerce threats demands a proactive approach to safeguarding consumers. These attacks can have devastating consequences, ranging from identity theft to significant financial losses. Understanding the potential impact and implementing effective mitigation strategies is crucial for both individuals and businesses.
Potential Impact on Consumers
Consumers are vulnerable to a multitude of detrimental effects from malicious e-commerce activities. Data breaches can lead to the compromise of sensitive personal information, including credit card details, social security numbers, and addresses. This compromised data can be used for fraudulent activities, such as unauthorized purchases, identity theft, and the opening of fraudulent accounts. Financial losses can be substantial, impacting not only the immediate financial well-being of the consumer but also their long-term credit standing.
Beyond financial harm, the emotional toll of a data breach can be significant, affecting trust in online transactions and the digital world in general.
Safe Online Practices for Consumers
Protecting yourself from these threats requires adopting strong online habits. Firstly, strong, unique passwords for each online account are paramount. Avoid reusing passwords across multiple platforms, as this significantly increases vulnerability. Regularly updating software and operating systems is critical, as outdated systems are often easier targets for attackers. Be wary of suspicious emails, links, or websites.
Verify the authenticity of any request for personal information before responding.
Spotting Suspicious Emails, Links, or Websites
Critically evaluate the origin of emails, links, and websites. Look for inconsistencies in grammar, spelling, or formatting. Pay close attention to the sender’s email address and the website’s URL. Genuine organizations typically have recognizable and secure URLs. Hovering over links before clicking them reveals the actual destination URL.
If the destination URL doesn’t match the displayed text or the context of the message, it’s likely a phishing attempt. Be cautious of urgent requests for personal information, as legitimate institutions rarely employ such tactics.
E-commerce Company Responsibilities
E-commerce companies have a crucial role in protecting their customers. Transparency and proactive communication are essential. Clearly informing customers about potential threats and providing readily available support channels are vital. This includes providing resources on how to recognize phishing attempts and offering steps to secure accounts. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments should be conducted to proactively identify and address potential weaknesses in their systems.
Tips for Maintaining Safe Online Shopping Habits
- Verify Website Security: Look for the padlock icon in the browser’s address bar, indicating a secure connection (HTTPS). Ensure the website’s URL is legitimate and not a deceptive imitation.
- Review Order Summaries Carefully: Thoroughly review all order summaries before confirming a purchase. Double-check the items, quantities, and prices. Any discrepancies should raise suspicion.
- Use Strong and Unique Passwords: Employ strong passwords for all online accounts and avoid reusing passwords across different platforms. Utilize password managers to create and store complex passwords securely.
- Be Wary of Urgent Requests: Avoid responding to emails or messages that create a sense of urgency, especially those demanding immediate action or personal information.
- Report Suspicious Activity: Report any suspicious emails, links, or websites to the appropriate authorities and the platform hosting the site.
Industry Response and Recommendations: Security Firm Warns Of New E Commerce Threat
E-commerce platforms are facing a rapidly evolving threat landscape. The security firm’s analysis highlights the need for proactive measures beyond reactive patching. Companies must adopt a holistic approach to security, encompassing not only technology but also operational procedures and a culture of vigilance. This requires a deep understanding of the specific vulnerabilities and a commitment to adapting to the changing nature of cyberattacks.The security firm’s analysis underscores the crucial role of ongoing threat intelligence in anticipating and mitigating emerging e-commerce threats.
By proactively identifying patterns and vulnerabilities, companies can implement targeted defenses and reduce their exposure to potential attacks. This proactive approach to security is essential for safeguarding both businesses and customers.
Threat Identification Methodology
The security firm employed a multi-faceted approach to identify the new e-commerce threat. This involved analyzing public and private datasets of known vulnerabilities, reviewing incident reports from various e-commerce platforms, and conducting penetration testing on simulated e-commerce environments. Real-world data from compromised systems was instrumental in pinpointing the attack vectors and exploiting vulnerabilities. By combining these methods, the firm developed a comprehensive understanding of the attack methodology and the specific vulnerabilities that were being targeted.
Recommendations and Warnings
The security firm issued a series of crucial warnings and recommendations. They emphasized the need for robust authentication measures, including multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strong password policies. The firm also highlighted the importance of regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address potential weaknesses. Finally, the security firm stressed the importance of educating employees about phishing attempts and other social engineering tactics.
Security firms are sounding the alarm about a new, sneaky e-commerce threat. It’s a worrying trend, reminiscent of how early online businesses, like the one that swallowed up CDNow, Columbia House swallows up cdnow , faced similar vulnerabilities. The new threat highlights the ever-evolving nature of online security risks, emphasizing the need for constant vigilance and updated protection measures.
These recommendations aim to create a layered defense system against sophisticated cyberattacks. Furthermore, they stressed the critical importance of security awareness training for all employees.
A security firm just issued a warning about a new e-commerce threat, highlighting the ever-evolving nature of online risks. Meanwhile, a coalition is actively lobbying against burdensome e-commerce taxes, which could potentially impact the very companies targeted by this new threat. This highlights a complex interplay between security concerns and regulatory pressures, all while emphasizing the need for robust e-commerce security measures to keep up with this ongoing battle.
coalition lobbies against onerous e commerce taxes It seems the fight against online threats is far from over.
Comparison of E-commerce Company Approaches
Different e-commerce companies exhibit varying degrees of preparedness and response to security issues. Some companies have invested heavily in advanced security technologies and employ highly skilled security teams. Others have a more reactive approach, often addressing security concerns only after a breach occurs. This disparity in approach underscores the need for industry-wide standards and best practices to ensure a consistent level of security across the board.
For example, companies like Amazon have demonstrated a proactive approach to security by investing in sophisticated security systems and developing innovative security solutions.
A security firm just issued a warning about a new threat targeting e-commerce platforms, highlighting the ever-present dangers in the digital world. While e-commerce is clearly giving Lands’ End a boost, as seen in e commerce gives lands end a boost , it’s crucial to remember that this growth comes with increased vulnerability. This new threat underscores the need for businesses to stay vigilant and implement robust security measures to protect themselves and their customers.
Role of Industry Standards and Regulations, Security firm warns of new e commerce threat
Industry standards and regulations play a critical role in preventing e-commerce threats. Compliance with standards like PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) is crucial for protecting sensitive customer data. Regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) further enhance the protection of personal information. The presence of strong regulations and standards encourages companies to implement robust security measures and helps to establish a baseline of security across the industry.
Compliance with these regulations is vital for maintaining trust with customers.
Proactive Steps for Strengthening E-commerce Security
To bolster e-commerce security, the industry should take a series of proactive steps. These steps should encompass the following:
- Strengthening Authentication Procedures: Implementing robust multi-factor authentication (MFA) across all platforms, especially for critical transactions and account access, is paramount.
- Investing in Advanced Security Technologies: Integrating advanced security tools like intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) systems to identify and respond to threats in real time is essential.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Regularly assessing systems for vulnerabilities through rigorous audits and penetration testing is critical to proactively identify and address weaknesses before they can be exploited.
- Employee Security Awareness Training: Educating employees about phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and other security threats through comprehensive training programs is vital to preventing human error in security.
- Collaboration and Information Sharing: Encouraging collaboration and information sharing among e-commerce companies and security experts to identify emerging threats and share best practices is a crucial aspect of proactive security.
Technical Analysis and Prevention
The new e-commerce threat leverages sophisticated techniques to exploit vulnerabilities in online platforms. Understanding these technical components is crucial for developing effective countermeasures. This analysis delves into the specific methods employed by attackers, along with actionable steps for robust prevention strategies.This threat exploits a combination of vulnerabilities, including weak authentication protocols, insecure payment gateways, and poorly configured web servers. These vulnerabilities are often exacerbated by insufficient security training for personnel involved in development and deployment.
Technical Components of the Threat
The new threat vector utilizes compromised third-party libraries, malicious scripts injected into legitimate e-commerce sites, and credential stuffing attacks targeting user accounts. These attacks often rely on sophisticated techniques to bypass traditional security measures. Attackers frequently exploit vulnerabilities in APIs and other software interfaces to gain unauthorized access.
Implementing Security Measures
Implementing robust security measures is paramount. This involves multi-layered security protocols. Regular security audits of all systems and applications are essential to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Secure Coding Practices: Adhering to secure coding principles throughout the software development lifecycle is crucial. This includes input validation, parameterized queries, and secure session management. Developers should be trained to identify and avoid common coding errors that attackers exploit. For instance, neglecting to sanitize user input can lead to cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. This can be mitigated through rigorous input validation procedures.
- Vulnerability Management: Proactive vulnerability management is vital. Regular scans for known vulnerabilities in software libraries and frameworks are necessary. This should be integrated into the software development lifecycle to identify and address issues early. Continuous monitoring of systems for suspicious activity is also crucial.
- Strong Authentication and Authorization: Implementing strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), is essential. Restricting access based on user roles and privileges is also crucial. Using strong, unique passwords and enforcing password complexity rules can help prevent brute-force attacks.
Secure Coding and Software Development
Adopting secure coding practices is a critical aspect of preventing this threat. It’s not just about fixing vulnerabilities; it’s about building security into the foundation of the application. Security should be considered at every stage of the software development lifecycle.
- Input Validation: Validate all user inputs to prevent injection attacks, such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). Always sanitize user inputs before using them in queries or displaying them on the website. Sanitization techniques can involve escaping special characters or using parameterized queries.
- Output Encoding: Encode all outputs to prevent reflected XSS attacks. This means converting potentially harmful characters into their HTML entities.
- Secure Libraries and Frameworks: Utilize updated and vetted libraries and frameworks to avoid known vulnerabilities. Regularly update these components to patch security flaws. Stay informed about security advisories for commonly used libraries and frameworks.
Cybersecurity Tools
Various cybersecurity tools can be used to prevent or detect this threat. These tools provide a layered defense approach.
| Tool | Function | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) | Filter malicious traffic and protect against various attacks, including SQL injection and cross-site scripting. | High |
| Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) | Monitor network traffic for malicious activity and block suspicious patterns. | Medium to High |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems | Collect and analyze security logs from various sources to detect anomalies and potential threats. | High |
| Vulnerability Scanners | Identify known vulnerabilities in applications and infrastructure. | Medium to High |
| Penetration Testing Tools | Simulate real-world attacks to assess the security posture of systems and applications. | High |
Final Summary
In conclusion, the new e-commerce threat necessitates a proactive and multifaceted approach to security. Businesses must prioritize vulnerability assessments and implement robust security measures, including the use of secure coding practices, updated software, and robust cybersecurity tools. Consumers should also be vigilant, practicing safe online habits and being wary of suspicious emails and websites. Ultimately, a collective effort from businesses and consumers is essential to combat this evolving threat landscape and ensure the continued safety and security of online transactions.






